افتادگی پلک چیست ؟
این بیماری به افتادگی پلک فوقانی اطلاق شده و می تواند یک یا هر دو پلک را در گیرد . در فرم خفیف بیماری افتادگی پلک در حد بالای مردمک چشم می باشد ولی در موارد شدیدتر افتادگی پلک منجر به پوشاندن قسمتی از مردمک شده به طوری که میدان بینایی فوقانی را کاهش می دهد .
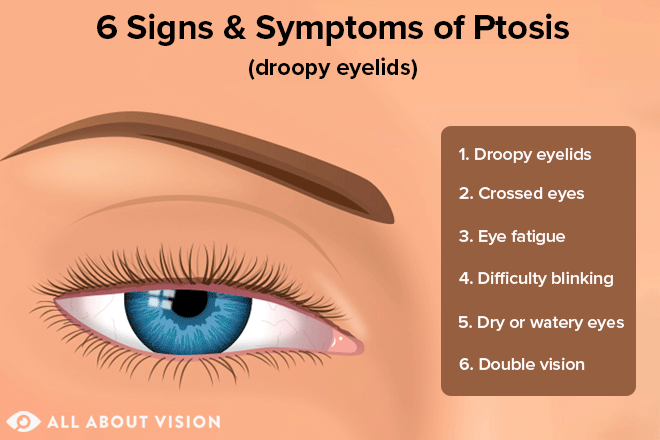
پتوز می تواند یک یا هر دو چشم را درگیر کند. وراثتی باشد.در بدو تولد بروز کند.در سنین بالاتر اتفاق بیفتد.
بارزترین علامت پتوز یا بلفاروپتوز خود افتادگی پلک است. سایر علائم عبارتند از مشکل در باز کردن چشم یا نیاز به کج کردن سر به عقب برای بهتر دیدن. خستگی چشم، انحراف چشم، یا دوبینی نیز میتوانند به همراه پتوز ( افتادگی پلک فوقانی ) اتفاق افتند.
علل افتادگی پلک چشم گوناگونند. برخی ممکن است با افتادگی چشم موروثی متولد شوند، که به آن پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) مادرزادی گفته میشود. اکثر موارد پتوز اکتسابی با بالا رفتن سن و در نتیجه کشیده شدن و شل شدن تاندونی که پلک را باز نگه میدارد، ایجاد میشوند.
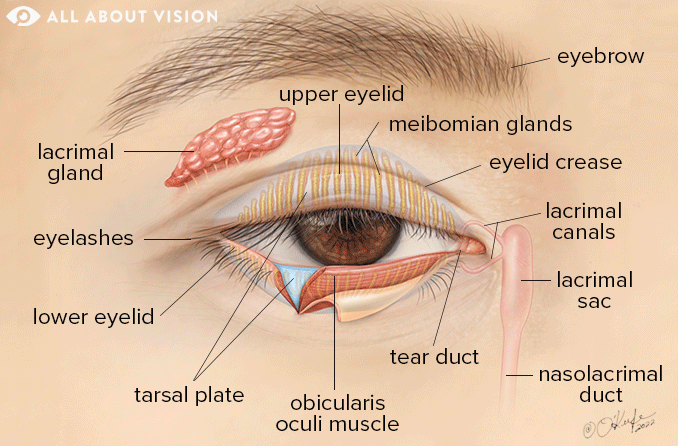
Eyelid Structures
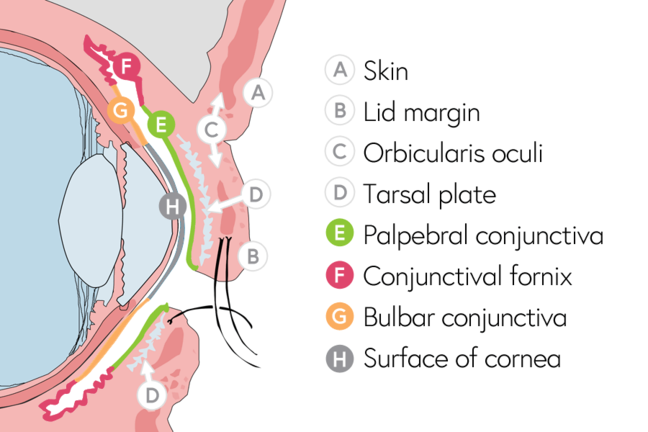
SKIN
The eyelid skin is the thinnest in the body.
The skin contains fine hairs, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands.
EYELID FOLDS
In non-Asians, the levator palpebrae superioris muscle has some attachments to the upper border of the tarsus, which forms a superior eyelid fold.
In non-Asians, the levator palpebrae superioris muscle does not have these attachments, so the superior eyelid fold is minimal or absent.
SUBCUTANEOUS CONNECTIVE TISSUE

various layers of the eyelid :
- Skin
- Subcutaneous connective tissue (the Oculoplastics BCSC book lumps the skin and subcutaneous tissue into one layer, as clinically they are fairly indistinct)
- Orbicularis oculi muscle
- Orbital septum
- Levator palpebrae superioris muscle (not present in the lower eyelid)
- Müller muscle (inferior tarsal muscle in the lower eyelid)
- Tarsus
- Conjunctiva
TYPES OF PTOSIS [7]
According to the onset of ptosis can be:
• intrinsic
• acquired
According to the cause it can be:
- Aponeurotic ptosis: It is most often involuntive as a result of the aging process. The upper eyelid is lowered on both sides and asymmetrically with worsening ptosis throughout the day. The upper eyelid levator muscle function is usually normal.
- Myogenic ptosis: It is caused by a disorder of the upper eyelid levator muscle itself or by a disorder at the neuromuscular junction. It is most often the first sign of myasthenia gravis disease. The eyelids are lowered on both sides and asymmetrically, worsening during the day and recovering after rest.
- Neurogenic ptosis: Most often it is unilateral, due to impaired brain nerve function responsible for eyelid movement or sympathetic nerves.
- Mechanical ptosis: It is caused by impaired motility of the upper eyelid with orderly nerve and muscle function.
- Traumatic ptosis is a consequence of the upper eyelid injury.
What is congenital ptosis [8]
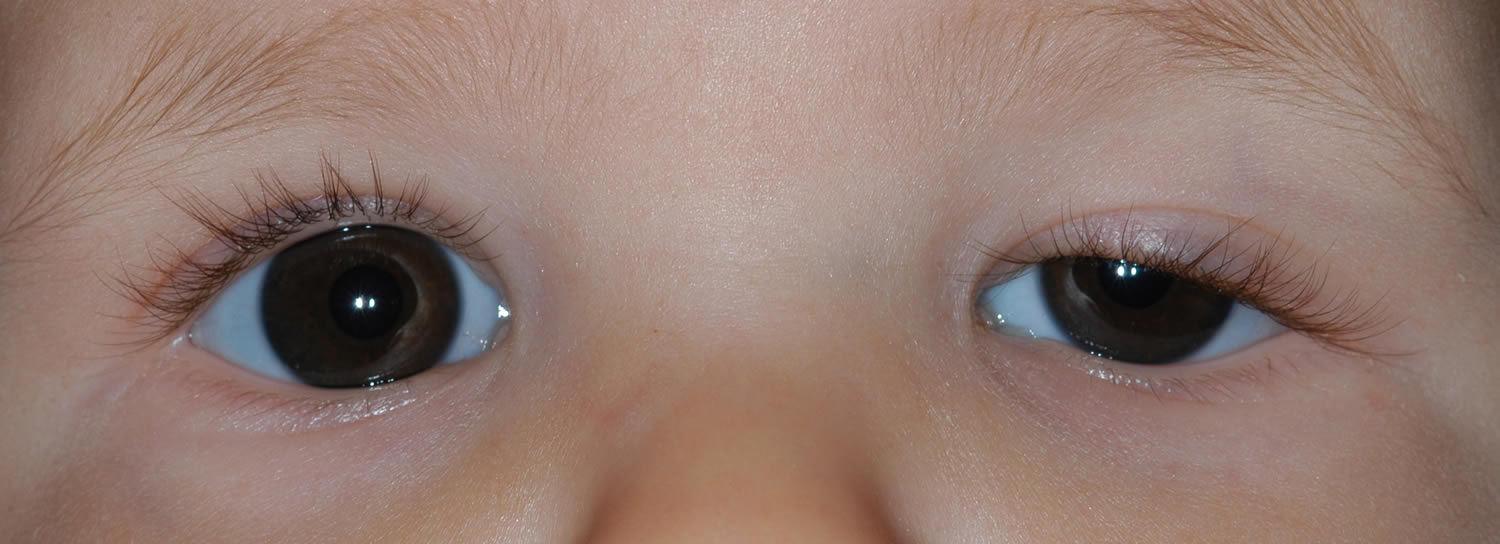
Congenital ptosis also called congenital blepharoptosis, is a drooping eyelid that is present at birth or within the first year of life. Congenital ptosis is usually present at birth but may manifest within the first years of life. In ptosis, the upper eyelid falls to a position that is lower than normal. In severe cases of ptosis, the drooping eyelid can cover part or all of the pupil and interfere with vision, resulting in amblyopia.
Amblyopia may result from obscuration of the vision directly or from development of astigmatism indirectly. Development of amblyopia is an indication for immediate surgical correction.
- Occlusion amblyopia
- Astigmatism from the compression of the droopy eyelid
- Ocular torticollis
In most cases of congenital ptosis, the problem is isolated and does not affect the vision. Any ptosis that develops over a period of days or weeks can signal a serious medical problem and needs further neurologic and physical evaluation.
Although not all patients with congenital ptosis need surgical intervention, patients need to be closely monitored for the possible development of deprivational amblyopia. Since amblyopia may not be reversed after age 7-10 years, appropriate and timely medical and surgical treatment of congenital ptosis is critical to preserve the child’s vision.
Scarless ptosis surgery before and after pictures
Ptosis is a drooping of the upper eyelid. A droopy eyelid can cause blurring of vision or watering of the eye due the weight of the eyelid pressing on the front of the eye.
Congenital ptosis causes
In most cases of congenital ptosis, the cause is idiopathic (unknown).
Histologically, the levator muscles of patients with congenital ptosis are dystrophic 1). The levator muscle and aponeurosis tissues appear to be infiltrated or replaced by fat and fibrous tissue. In severe cases, little or no striated muscle can be identified at the time of surgery. This suggests that congenital ptosis is secondary to local developmental defects in muscle structure.
Congenital ptosis may occur through autosomal dominant inheritance. Common familial occurrences suggest that genetic or chromosomal defects are likely.
Other potential causes of congenital ptosis include:
- Blepharophimosis syndrome: This condition consists of short palpebral fissures, congenital ptosis, epicanthus inversus, and telecanthus.
- Third cranial nerve palsy: Signs of aberrant regeneration are usually present. The pupil may be paradoxically small and nonreactive.
- Horner syndrome: Ipsilateral findings of mild ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis characterize this syndrome. The ipsilateral lower eyelid may be elevated. Also, because of the lack of sympathetic innervation to the iris melanocyte development, a difference in the iris color between the eyes may result (called heterochromia).
- Marcus Gunn jaw-winking syndrome: The motor nerve to the external pterygoid muscle is misdirected to the ipsilateral levator muscle. Lid elevation occurs with mastication or with movement of the jaw to the opposite side.
- Birth trauma
- Duane syndrome: In this condition, the sixth cranial nerve fails to innervate a lateral rectus muscle. Then, the muscle acquires an innervation of the third cranial nerve. Although the synkinesis produced does not involve lid innervation, enophthalmos with apparent ptosis may result. In Esotropic Duane syndrome, the upper eyelid droops further and the lower lid elevates when the eye is adducted because of a co-contraction of the horizontal rectus muscles.
- Periorbital tumor: Neuroblastoma, plexiform neuromas, lymphomas, leukemias, rhabdomyosarcomas, neuromas, neurofibromas, or other deep orbital tumors may produce ptosis or proptosis.
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome: This mitochondrial deletion disorder is characterized by progressive external ophthalmoplegia, heart block, retinitis pigmentosa, and central nervous system manifestations. This condition begins in childhood but is rarely present at birth. The conditions are most likely to become symptomatic in the first or second decade of life. Bilateral ptosis is a prominent feature of this syndrome.
- Myotonic dystrophy: Patients with this condition may present with polychromatic cataracts, gonadal atrophy, or premature thinning and/or loss of hair. Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disorder that is characterized clinically by myotonia and progressive muscular weakness. Frontal balding and temporalis muscle wasting are also clinically evident.
- Myasthenia gravis: A defect at the neuromuscular junction produces relative unresponsiveness to released acetylcholine, resulting in ptosis.
- Pseudotumor of the orbit: Patients with this condition may present with ptosis due to inflammation and edema of the eyelid.
- Pseudoptosis: Less tissue in the orbit (eg, unilateral smaller eye, fat atrophy, blowout fracture) produces the appearance of ptosis secondary to the decreased volume of orbital contents.
افتادگی پلک همچنین میتواند در اثر تروما، جراحی، یا آسیب به عضلاتی که پلک را بالا میکشند یا اعصابی که این عضلات را کنترل میکنند، اتفاق افتد. تومورها، اختلالات عصبی، بیماریهای سیستمیک، و برخی داروهای خاص نیز میتوانند باعث به وجود آمدن پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) شوند.
بسته به علت ایجاد آن، پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) میتواند به صورتهای زیر دستهبندی شود:
پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) نوروژنیک: به حالتی گفته میشود که اعصاب متصل به عضلات تحت تأثیر قرار بگیرند.
پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) میوژنیک: به حالتی گفته میشود که افتادگی پلک در اثر مشکلی در عضله ایجاد شده باشد که پلک را بالا میبرد.
پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) آپونوروتیک: به حالتی گفته میشود که تاندون مسئول لیفت پلک کشیده شده و ضعیف شده باشد.
پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) مکانیکال: به حالتی گفته میشود که سنگینی پلک برای عضلات خیلی زیادتر از آن است که بتوانند بلندش کنند.

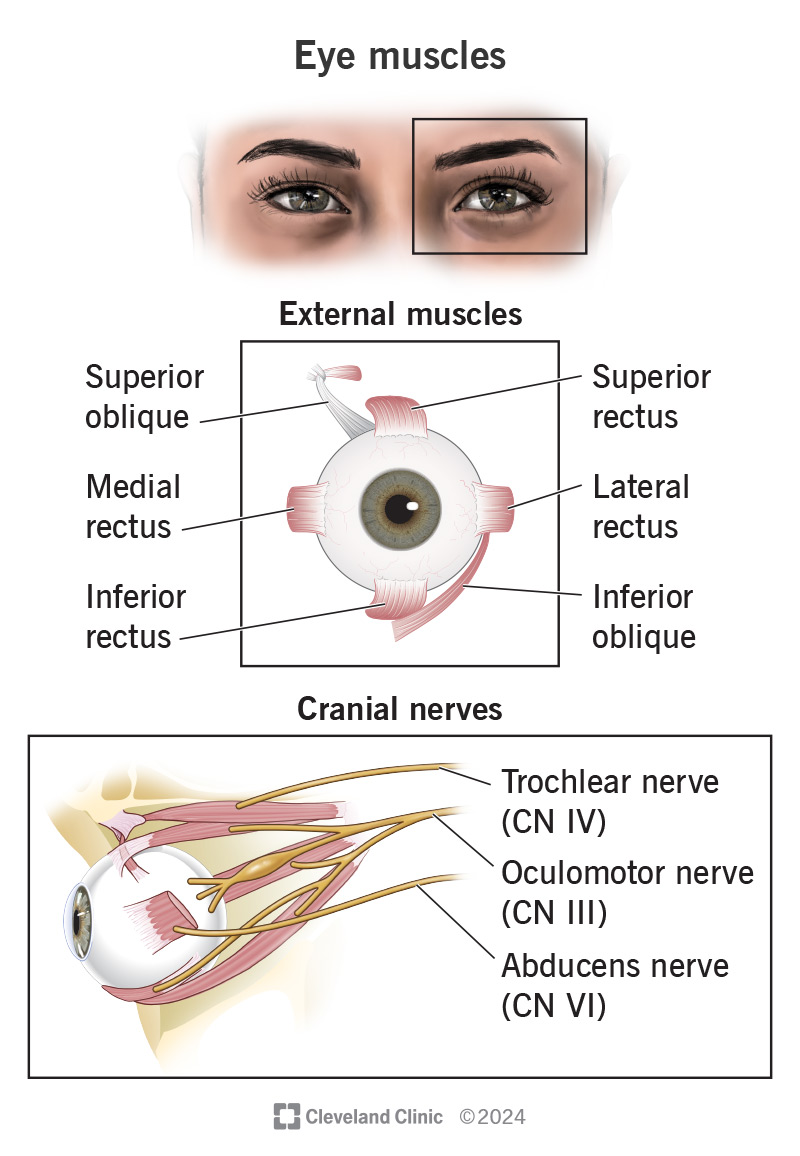
Extra-ocular muscles responsible for eye movement
عوامل متعددی ممکن است امکان ابتلای شما به پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) را افزایش دهند.
از قبیل:
- بالا رفتن سن
- زمینه خانوادگی ابتلا به پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی)
- آسیبهای ناشی از تولد
- جراحی چشم برای برداشتن آب مروارید
- فلج فیبرهای عصبی پلکها
- دیابت
- ضربه
- سندرم هورنر
- ترومای سر یا پلک
- تومور مغزی
- تحلیل و فساد عضلانی
- میاستنی گراویس
در برخی موارد، برای تعیین علت پتوز (افتادگی پلک فوقانی) اکتسابی، آزمایشات پزشکی انجام میپذیرد. از آنجا که چند دلیل برایافتادگی پلک وجود دارد، شدیداً توصیه میشود که حتی اگر علائم خفیف باشند، برای تشخیص به پزشک مراجعه کنید.
پتوز در کودکان
پتوز مادرزادی به معنای وجود پتوز در بدو تولد می باشد. اگر کودکی با پتوز متوسط تا شدید متولد شود، ممکن است برای تکامل بینایی نیازمند درمان فوری باشد.
پتوز مادرزادی اغلب در اثر نقص در تکامل عضله بالابرنده پلک فوقانی که عضله لواتور نام دارد، اتفاق می افتد. اگرچه معمولا یک اختلال مجزا می باشد، ولی در موارد مادرزادی، ممکن است همراه با اختلالات زیر باشد:
- اختلال حرکات چشمی
- بیماری های عضلانی
- تومورهای پلک یا سایر تومورها
- اختلالات عصبی
- عیوب انکساری
- پتوز مادرزادی معمولا با گذشت زمان بهبود نمی یابد.
چرا این بیماری رخ می دهد ؟
این بیماری می تواند در زمان تولد تظاهر کند که افتادگی پلک مادر زادی اطلاق می شود همچنین زمانی که عضلات بالا برنده پلک تشکیل نشده باشد افتادگی پلک مادر زادی است .در نوع ناشی از افزایش سن، تاندون عضلات با لا بر پلک از محل اتصا لشان بر روی پلک جدا شده و در نتیجه افتادگی پلک رخ می دهد که معمولا در سنین بالای ۰ ۵- ۴۵ سال رخ می دهد و در اثر پوست اضافی در پلک می باشد .
علائم و نشانه های پتوز کدامند؟
شایعترین علامت آشکار پتوز در کودکان، افتادگی پلک می باشد. در پتوز مادرزادی، اغلب عدم تقارن چین پلک فوقانی وجود دارد. کودکان مبتلا به پتوز ممکن است برای دیدن مجبور شوند گردن خود را به عقب خم کنند یا ابروها را به سمت بالا بکشند. این مانورهای سر و صورت نشان می دهند که کودک سعی می کند برای دیدن از هر دوچشم استفاده نماید. بعد از گذشت چند سال، این وضعیت های غیر طبیعی سر ممکن است منجر به اختلالات ظاهری سر و گردن شوند.
مشکلات ناشی از پتوز در کودکان کدامند؟
شایع ترین اختلال جدی مرتبط با پتوز دوران کودکی، آمبلیوپی (تنبلی چشم) می باشد. به دو علت پتوز می تواند ایجاد تنبلی چشم کند:
- انسداد مسیر بینایی در موارد پتوز شدید
- ایجاد آستیگماتیسم و تاری دید ناشی از آن
بعلاوه پتوز ممکن است در صورت وجود انحراف چشم آن را مخفی نماید و این مورد نیز می تواند منجر به تنبلی چشم شود.
Causes & Risk Factors [2]
While most often caused by aging, there are a variety of underlying health conditions and other complications that can cause ptosis.
- Age
- Injury or trauma
- Infection or tumor of the eyelid
- Tumor inside the eye socket
- Side effect of cataract surgery
- Side effect of corrective eye surgery, like LASIK, PRK, LASEK, RLE and others
- Levator muscle problems
- Eye tumor
- Diabetes
- Myasthenia gravis, a rare and progressive muscle weakness disorder.Eyelid drooping is often a first sign of this condition.
- Muscle disease like muscular dystrophy
- Brain tumor
- Stroke
- Brain aneurysm
- Horner’s syndrome
- Cancer of the nerves
- Bell’s palsy
- Side effect of a Botox injection
about Ptosis Repair
Ptosis repair by external levator advancement should be performed in the operating room under monitored anesthesia care. As the patient's cooperation is required for portions of the procedure, excessive sedation should be avoided.

(a,b) Upper eyelid ptosis repair with knotted sutures (Genova et al., 2005)
Management of Complications
- Undercorrection: Undercorrection of eyelid ptosis is one of the most common complications in ptosis repair. If noted within the first 3 to 4 days and edema is minimal, the patient can be taken back to the operating room for an adjustment. If undercorrection is noted after 4 days, the patient should be followed at least 6 months before a second operation is performed.
- Overcorrection: Overcorrection of eyelid ptosis presents as lagophthalmos and can lead to corneal exposure and dry eyes; it should at minimum be treated with ophthalmic saline drops 3 to 4 times during the day and with ophthalmic ointment at bedtime. If the lagophthalmos is mild, you can treat conservatively with eyelid massage several times throughout the day. A temporary tarsorrhaphy suture may be utilized while the swelling resolves and the tissues are softened with scar massage. If the overcorrection is severe or if corneal injury is present or symptoms fail to improve within 1 to 2 weeks with conservative treatment, surgical correction is required.
- Corneal abrasion: Corneal abrasions can occur as a result of injury to the eye during surgery or post-operatively as a result of incorrectly placed sutures that irritate the eye. This is treated with ophthalmic antibiotic drops or ointment four times per day until fully healed. If the corneal abrasion is due to an incorrectly placed suture, the suture should be adjusted to avoid further corneal injury. If the corneal abrasion is severe, significant scarring can lead to decreased vision.
- Infection: Infections of the eyelid after surgery are uncommon but should be treated with oral antibiotics. If an abscess is present, incision and drainage of the site is necessary.
- Retrobulbar hematoma: Retrobulbar hematomas are extremely rare but can lead to blindness if not diagnosed and treated early. This is caused by bleeding into the post-septal compartment of the eye, resulting in acute onset of severe pain, proptosis, decreased vision and extraocular movements, dilated pupils, scotomas, and increased ocular pressure. The treatment of this condition is emergent and requires surgical exploration to evacuate the hematoma and obtain hemostasis. A lateral canthotomy under local anesthesia can be performed at the bedside while the patient is waiting to be transferred to the operating room.
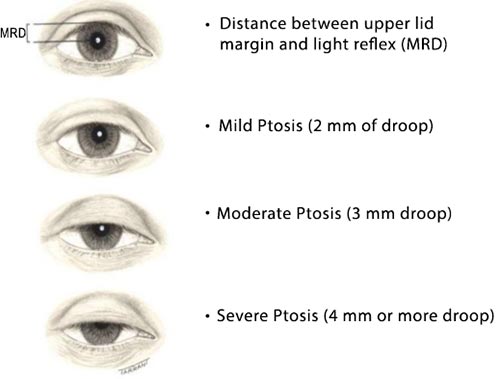
Key Principles
- The upper eyelid margin normally lies 0.5 to 2 mm below the superior corneal limbus. Ptosis describes the descent of the upper eyelid margin below the normal anatomical position and is classified as mild (1–2 mm), moderate (3–4 mm), and severe (>4 mm).
- Hering's test: The Hering's test attempts to expose hidden contralateral ptosis. Manually elevating the ptotic eyelid with a cotton-tip applicator to normal position will normalize the increased neural input and unmask hidden ptosis of the contralateral eyelid, if it exists.The law proposes that conjugacy of saccades is due to innate connections in which the eye muscles responsible for each eye's movements are innervated equally. The law also states that apparent monocular eye movements are actually the summation of conjugate version and disjunctive (or vergence) eye movements.
- Fasanella-Servat or conjunctival-Mullerectomy procedures are indicated in patients with mild ptosis and moderate to good levator muscle excursion.
- Levator advancement procedure is indicated in patients with attenuation or dehiscence of the levator aponeurosis associated with mild to severe ptosis and moderate to good levator muscle excursion.
- Frontalis sling procedure is indicated in ptosis patients with poor levator function and intact frontalis muscle. This is commonly performed in children with congenital ptosis.[4]
پتوز مادرزادی چگونه درمان می شود؟
در اغلب موارد، پتوز کودکان با جراحی درمان می شود. اگر تنبلی چشم هم وجود داشته باشد، ممکن است درمان با قرار دادن پوشش بر روی چشم سالم، استفاده از عینک یا قطره چشمی ضروری باشد. تشخیص لزوم انجام جراحی و انتخاب روش مناسب،
بر اساس عوامل زیر صورت می گیرد:
- سن کودک
- درگیری یک یا هر دو پلک
- شدت پتوز
- قدرت عضلات بالا برنده و پایین آورنده پلک
- وضعیت حرکات چشمی
در اوایل دوران زندگی معمولا ضرورتی به انجام جراحی برای موارد خفیف تا متوسط پتوز وجود ندارد. هم در موارد مذکور و هم موارد شدیدی که تحت عمل جراحی قرار گرفته اند، باید به طور منظم از نظر تنبلی چشم، عیوب انکساری و حالت های وابسته توسط چشم پزشک بررسی و در صورت نیاز تحت درمان قرار گیرند. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- spring 2012
علل پتوز بالغین چیست؟
شایعترین علت پتوز در بالغین، کشیدگی یا جداشدگی تاندون عضله لواتور از روی پلک می باشد. وقوع این فرایند ممکن است ناشی ازعلل زیر باشد:
- افزایش سن
- به دنبال جراحی کاتاراکت (آب مروارید) یا سایر جراحی های چشمی
- ضربه به چشم
پتوز بالغین همچنین ممکن است عارضه ای از سایر بیماری ها مانند بیماری های عصبی یا عضلانی و در موارد نادر تومورهای حدقه چشم باشد که عضله بالابرنده پلک یا عصب آن را درگیر می کنند
پتوز چشم راست- بعد از عمل
پتوز بالغین چگونه درمان می شود؟
چشم پزشک می تواند بررسی جامعی از مشکل شما به عمل آورده و راجع به روش های درمانی مختلف و عوارض وخطرات احتمالی آن ها اطلاعات لازم را در اختیار شما قرار دهد.
برای تشخیص علت پتوز و انتخاب بهترین روش درمانی ممکن است نیاز به انجام آزمایش خون، عکسبرداری های مخصوص و یا سایر آزمایشات باشد. در صورت یافتن علت زمینه ای باید ابتدا این مورد اصلاح گردد، اما در اغلب موارد، درمان نهایی جراحی است که نوع جراحی نیز بر اساس شدت پتوز و سایر یافته های بالینی تعیین می گردد.
Before surgery
A thorough examination should be performed preoperatively to exclude certain diseases for which surgery is not indicated.
Before the surgery, the following should be done / prepared:
• complete blood count
• small coagulogram
• allergy list (pay special attention to medication allergies)
• list of medications the patient is consuming (special attention should be paid to blood thinners such as: Aspirin, Andol, Martefarin, Warfarin, Heparin, etc.).

During the surgery
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia in adults. It lasts from 45 to 90 minutes, depending on whether surgery involves both eyelids. The surgeon makes an incision in the anterior ocular fold of the eyelid. Stitches are inserted into the muscle to strengthen its attachment to the eyelid and adjust the height of the eyelid.
After the surgery
After the ptosis surgery, it is necessary to limit certain activities for two weeks. It is also recommended to avoid eye rubbing or do anything that may cause eye irritation. The eyelid may be slightly swollen after the surgery and the eye may not be able to close completely within the first few of days.[7]
درمان این بیماران با عمل جراحی صورت می گیرد جراحانی که در این عمل مهارت دارند می توانند جراحی را تحت بیحسی موضعی انجام دهند ولی گاهی تحت بیهوشی عمومی هم صورت می گیرد. در طی این عمل اتصال عضله بالا برنده پلک با محل اتصالشان بر روی پلک مجددا برقرار می شود ولی به طور شایعتر در نوع مادر زادی عضله را کوتاه می کنند عمل اصلاح افتادگی پلک عمل بسیار ظریفی است و مدت زمان آن برای هر چشم ۴۵ دفیفه تا یک ساعت می باشد . در افتادگی پلک ناشی از افزایش سن اکثرا نیاز به عمل بلفاروپلاستی ( برداشتن پوست اضافه پلک ) نیز وجود دارد .
خطرات جراحی پتوز کدامند؟
خطرات جراحی پتوز شامل عفونت، خونریزی و کاهش بینایی می باشد، ولی وقوع این عوارض بسیار نادر است. بلافاصله بعد از عمل، ممکن است چشم بطورکامل بسته نشود، ولی این عارضه معمولا مقطعی است. در طی این مدت می توان از قطره و پماد برای محافظت چشم استفاده نمود. اگرچه ظاهر پلک بطور قابل توجهی اصلاح می شود، اما ممکن است پلک ها کاملا قرینه به نظر نرسند. در اغلب موارد بعد از جراحی در نگاه به پایین پلک عمل شده نسبت به طرف مقابل مختصری بالاتر قرار می گیرد و شب ها مختصری باز می ماند که این دو عارضه مشکل آفرین نیستند. در موارد نادر، حرکات کامل پلک قابل برگشت نیست. در برخی موارد، ممکن است بیش از یک بار عمل جراحی لازم باشد.
توصیه ׃
بیمار میبایست دو هفته قبل از عمل جراحی داروهایی که شانس خونریزی حین عمل یا پس از عمل جراحی را افزایش می دهند مثل آسپیرین، دیکلوفناک، بروفن، وارفارین ، …… را قطع نماید .
خلاصه
پتوز در بالغین و کودکان با انجام جراحی قابل درمان است و این درمان علاوه بر اصلاح وضعیت ظاهری می تواند باعث بهبود بینایی نیز شود. در پتوز کودکان، انجام معاینات منظم چشم پزشکی در سال های اول زندگی برای پیشگیری و درمان تنبلی احتمالی چشم از اهمیت ویژه ای برخوردار است.
Reference:
- pezeshkan.org
- draxe.com/ptosis
- ninitime.com/several-eyelid-drainage-therapies
- sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/ptosis-eyelid
- sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/ptosis-repair
- ophthalmologyreview.org/bcsc-fundamentals/eyelid-anatomy
- knezovic.com.hr/en/services/oculoplastic-and-aesthetic-procedures/ptosis
- healthjade.net/congenital-ptosis








 1)
1) 




















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/blepharitis-5201907-FINAL-3927570aef824ed4bc1fde18b0df2869.jpg)

 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.