اشتارگات (به انگلیسی: Stargardt disease) یک بیماری ژنتیک نادر است که باعث اختلال بینایی در مرکز شبکیه چشم میشود.
Stargardt disease is the most common form of inherited juvenile macular degeneration, occurring in one in every 8,000 to 10,000 people worldwide. It causes gradual loss of central vision. It usually develops during childhood or adolescence, resulting in a loss of the central part of the visual field.[2]
عوامل ایجاد بیماری [1]
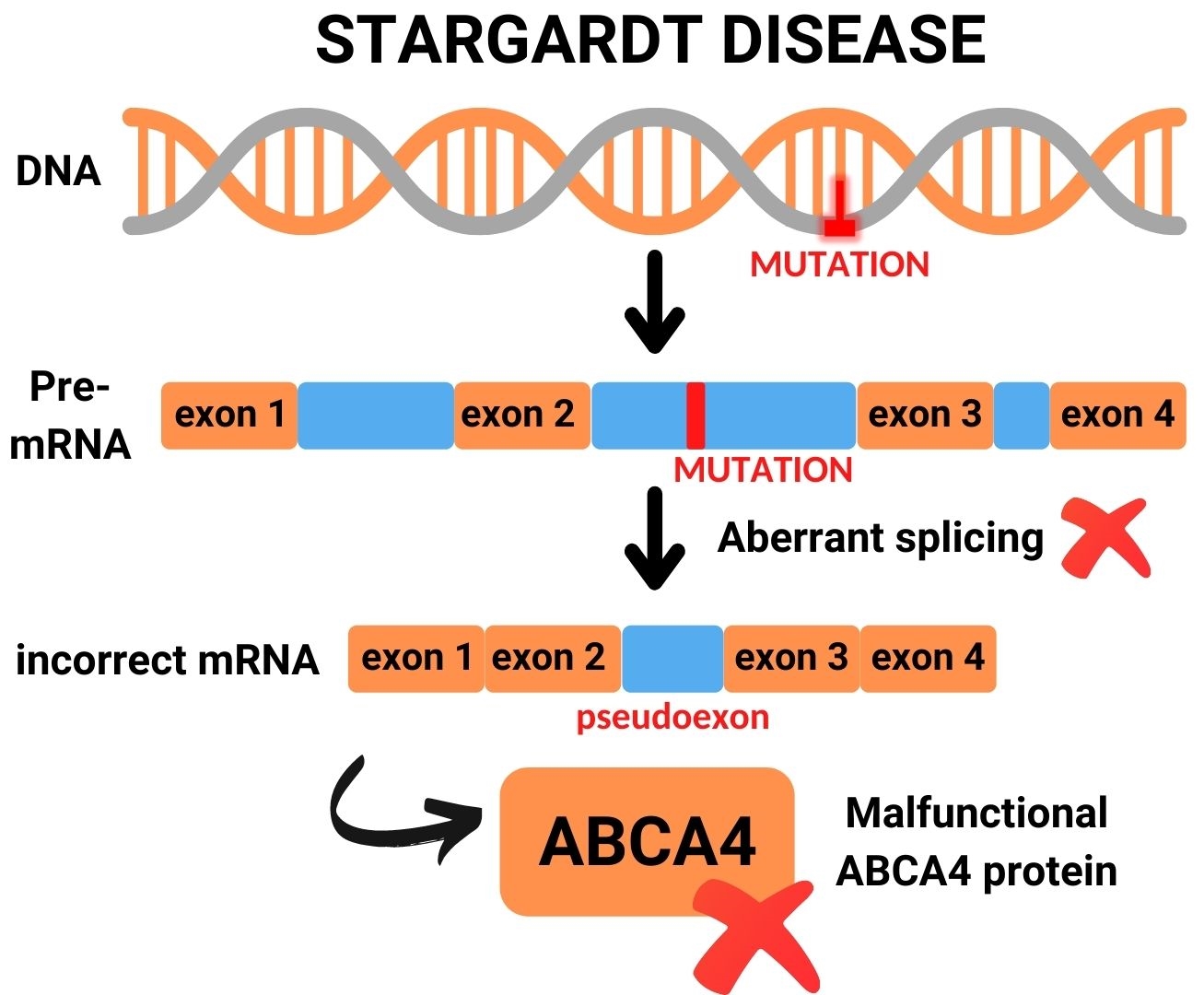
بیماری اشتارگارت یک مشکل مدیریت پسماند است، عامل ایجاد این بیماری نادر جهش در ژن ABCA4 میباشد، به این صورت که هم پدر و هم مادر باید حامل این ژن باشند تا به فرزند منتقل شود.
معمولاً در ازدواجهای فامیلی این جهش مشهود هست. دو نوع جهش ABCA4 موجود است.
در این جهشها سنتز ویتامین A مختل میشود و باعث تجمع پسامد در روی شبکیه شده و گیرندههای نوری سطح شبکیه را مختل میکند. ویتامین A یک عنصر مهم برای گیرندههای نوری سطح شبکیه چشم هستند.
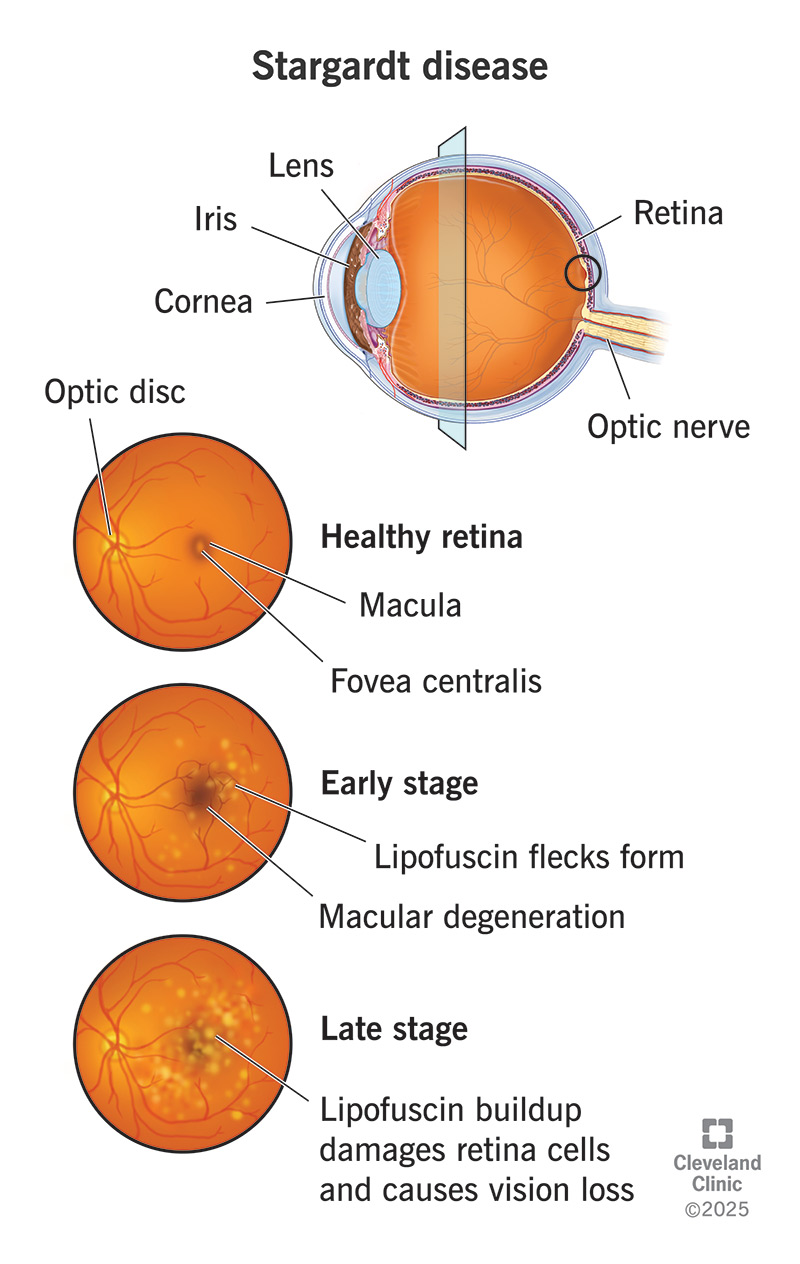
Stargardt disease is an inherited form of macular degeneration that first appears in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by progressive vision loss beginning in the macula, the central part of the retina where light falls and visual acuity and color vision are greatest.
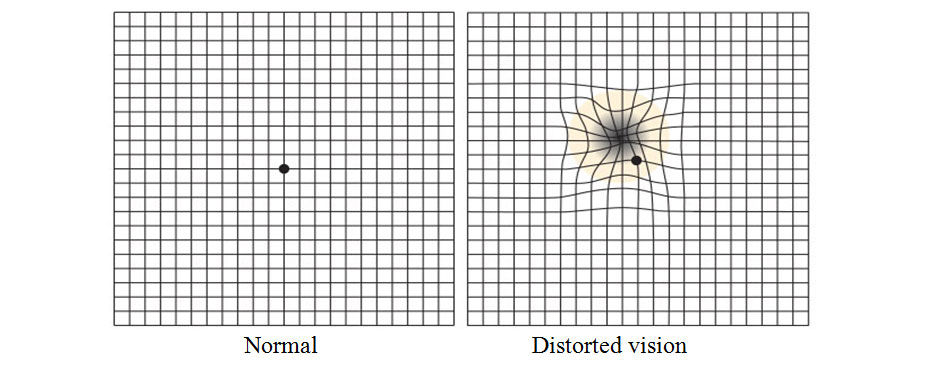
Symptoms include blurred or wavy vision, blind spots, impaired color vision, and difficulty seeing in low light situations. People with Stargardt disease are usually sensitive to glare.[2]
What are symptoms of Stargardts eye disease [3]
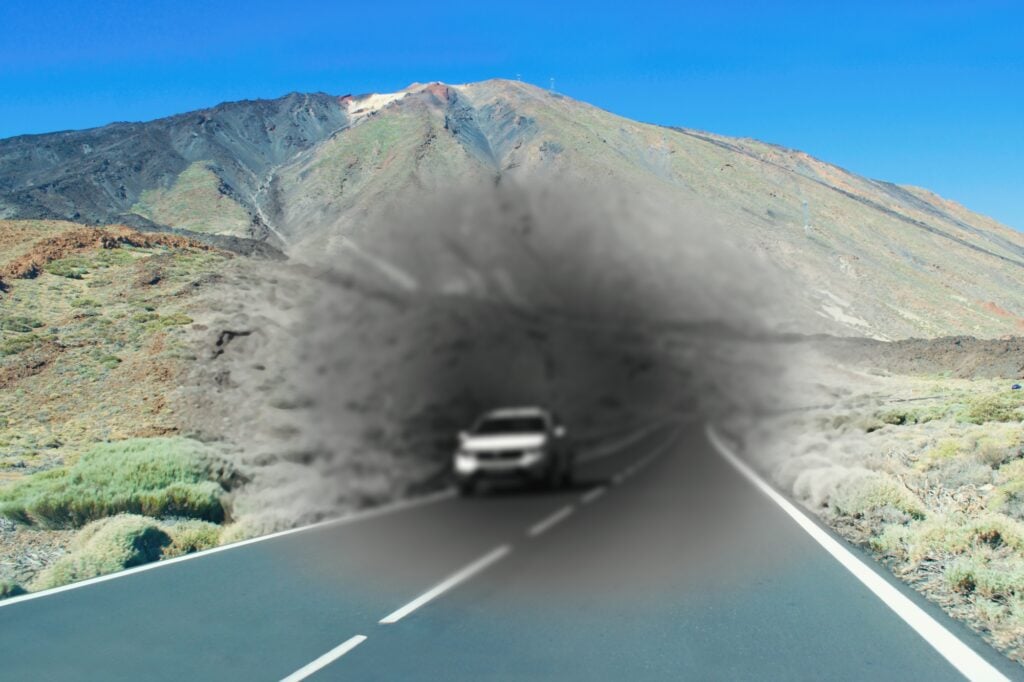
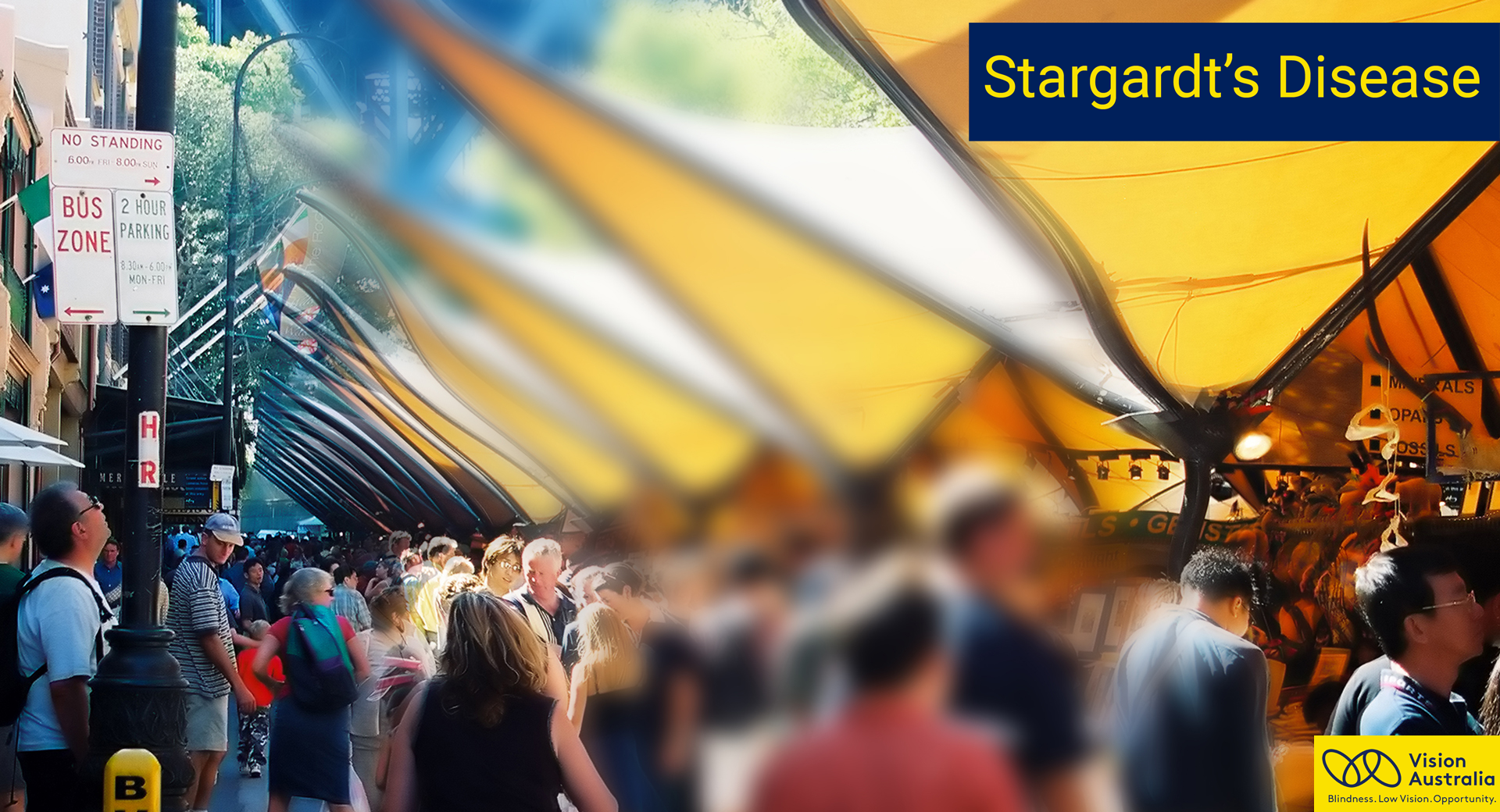
- Someone may initially become aware of an issue with their center vision. It may be distorted, hazy, or have black regions. Side vision (peripheral vision) is frequently unaffected. Colorblindness is a condition in which some individuals have difficulty perceiving colors.
- When moving between bright and dark environments, eyesight may take longer to adapt than normal.
- For some patients, Stargardt illness advances slowly at first, then quickly accelerates and finally plateaus. Vision loss may accelerate at roughly 20/40 vision (meaning someone sees at 20 feet what a normal-seeing person sees at 40 feet).
- While most persons with Stargardt illness eventually lose their central vision, many may have strong side vision for the remainder of their lives. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- autumn 2024
What can be done if Stargardt disease is diagnosed?
There is no cure for Stargardt disease, and there are no treatments.
What devices can help? Since the symptoms are underlying physiology of Stargardt disease are similar to those for other types of macular degeneration, people can usually benefit from the same devices as used for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). These help people retain independence in their homes, school, and jobs. Products include electronic magnifiers and devices that turn text into speech to read aloud mail, bills, books, and other printed materials. Freedom Scientific’s line of video magnifiers and screen magnification software can help.[2]
اشتارگات معمولا در کودکان، نوجوانان و بزرگسالان جوان ایجاد می شود. ممکن است شخصی ابتدا متوجه مشکلی در بینایی مرکزی خود شود. این مشکل معمولا تاری دید یا مشاهده نواحی تیره است. در این نوع بیماری چشمی دید جانبی یا محیطی معمولاً تحت تأثیر قرار نمی گیرد. اما برخی از افراد ممکن است در دیدن رنگ ها نیز مشکل داشته باشند. بیماری اشتارگات در برخی افراد ممکن است به کندی پیشرفت کند، سپس سرعت گیرد و به سرعت سطح بینایی را به میزان قابل توجهی کاهش دهد. با توجه به اینکه در بیماری اشتارگات از دست دادن بینایی می تواند به صورت ناگهانی سرعت خود را افزایش دهد، بنابراین در صورتی که با علائم اولیه مانند تاری دید یا مشاهده نواحی تیره مواجه شدید، باید سریعا به پزشک مراجعه کنید.
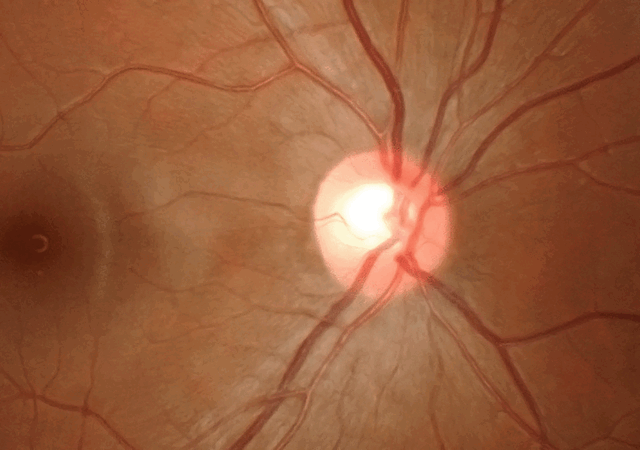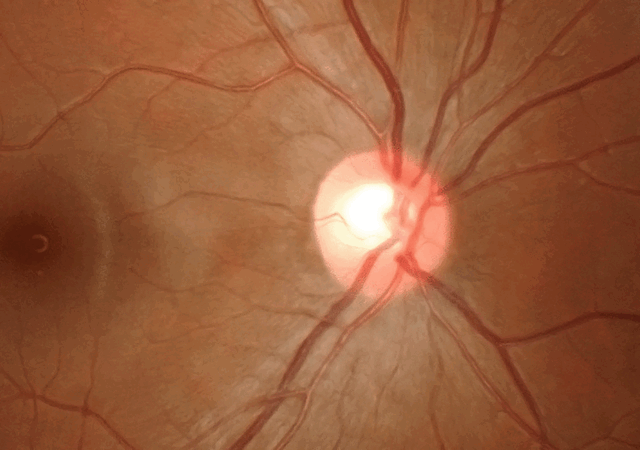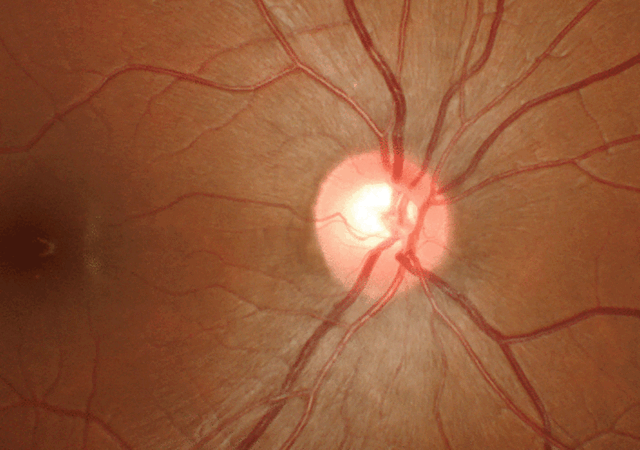
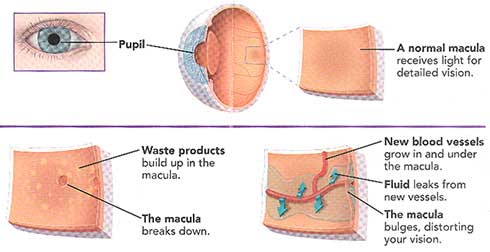
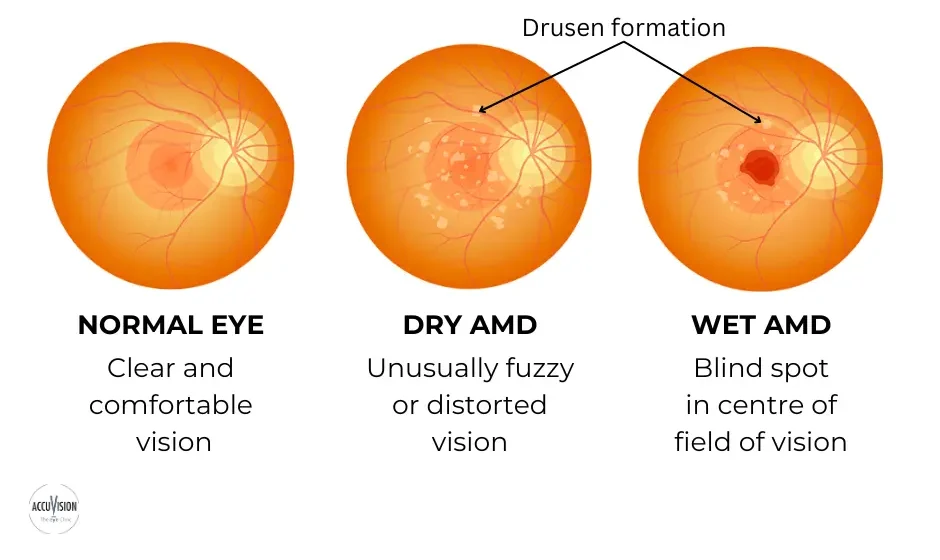
تغییر در بینایی مرکزی Central vision معمولاً منجر به تشخیص اولیه بیماری اشتارگات می شود. یک پزشک متخصص شبکیه چشم در حال معاینه شبکیه یک فرد مبتلا به بیماری اشتارگات ، لکه های زرد رنگ مشخصی را در RPE مشاهده می کند. لکه ها رسوبات لیپوفوسسین هستند که محصول جانبی فعالیت طبیعی سلول های شبکیه می باشند. با این حال، در این بیماری، لیپوفوسین به طور غیر طبیعی تجمع می یابد.
نکته: “توجه داشته باشید که پیشرفت از دست دادن بینایی در بیماری اشتارگات متغیر است. حدت بینایی (قابلیت تشخیص جزئیات و شکل) ممکن است در ابتدا به آرامی کاهش یابد، سپس شتاب بگیرد و دوباره یکنواخت شود. همچنین معمولاً مقداری دید محیطی در فرد مبتلا باقی خواهد ماند.”

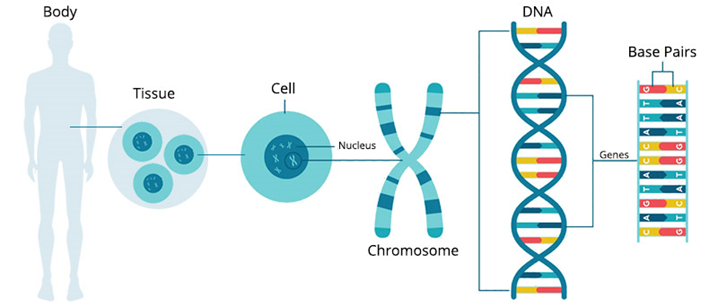
معمولاً بیماری اشتارگات از والدین منتقل می شود. در این بیماری، ژنهای معیوب (ژن ABCA4) برای داشتن علائم باید از هر دو والدین منتقل شود. هر کودک ۲۵ درصد ممکن است دو نسخه ABCA4 (یک نسخه از هر والدین) را که برای ایجاد این بیماری لازم است، به ارث ببرد. فردی که این ژن را فقط از یکی از والدین دارد، ناقل بیماری اشتارگات خواهد بود، اما علائمی نخواهد داشت. البته سایر اشکال بیماری اشتارگات برای ایجاد علائم تنها به ژن یکی از والدین نیاز دارند، اما این موارد بسیار نادر هستند. برای تشخیص دقیق این بیماری چشم پزشک معمولا از آزمایشی به نام آنژیوگرافی فلورسین استفاده می کند. در این آزمایش یک رنگ به بازوی شما تزریق می شود. از رنگ هنگام گردش در رگ های خونی شبکیه عکس گرفته می شود. در افراد مبتلا به اشتارگات عکس ها ناحیه تیره ای را در بافت شبکیه نشان می دهند. این به چشم پزشک کمک می کند تا بیماری اشتارگات را تشخیص دهد. همچنین در حال حاضر آزمایش ژنتیک برای تشخیص دقیق نوع دژنراسیون ماکولا در دسترس است. این مطمئن ترین راه برای دانستن مبنای ژنتیکی بیماری شما است.
بهترین گزینه برای جلوگیری از ابتلای فرزندان به بیماری اشتارگات انجام آزمایش ژنتیک است که به والدین در تشخیص قطعی بیماری و احتمال خطر ابتلای فرزندان به این بیماری کمک می کند. البته تا به امروز متاسفانه هیچ درمانی برای این بیماری وجود نداشته است. اما با این وجود چندین آزمایش ژن درمانی و دارودرمانی در حال انجام است. در ادامه به برخی از نکاتی که به افراد مبتلا به بیماری اشتارگات کمک می کند.
خوشبختانه اشتارگات یک بیماری ژنتیکی و نادر است که اغلب در کودکان تشخیص داده میشود. این بیماری به علت اشکال در ساختارهای استخوانی و بافتی در بدن ایجاد میشود. افراد مبتلا به اشتارگات ممکن است دارای قد کوتاهی، مشکلات در مفاصل و اندامهای حرکتی، اختلالات تنفسی، و مشکلات قلبی باشند. اشتارگات نیازمند مراقبت و مدیریت تخصصی پزشکی است. درمان این بیماری شامل جراحیها، فیزیوتراپی، و مراقبتهای پزشکی مخصوص میشود.

ارتقاء کیفیت زندگی افراد مبتلا به اشتارگات از طریق تیمهای درمانی و پشتیبانی اجتماعی انجام میشود تا به افراد این امکان داده شود تا با این بیماری مبارزه کنند و به حیات عادی نزدیکتر شوند.
درمان
سلول بنیادی
درمان قطعی برای بیماری اشتارگات در حال حاضر وجود ندارد، اما بیماری به وسیله ژن درمانی و سلول درمانی به وسیله سلولهای بنیادی قابل کنترل است و احتمال بهبود بیماری با ضریب بیشتری بالا میرود، استفاده از سلولهای بنیادی بستگی به زنده ماندن سلولهای بنیادی در محیط شبکیه چشم دارد، گاهی نیاز است در مقاطع زمانی مختلف درمان تکرار شود.
ویتامین آ
دانشمندان با جایگزین کردن اتمهای هیدروژن با دوتریوم Deuterium در ویتامین A توانستند Alk-001 را تولید کنند. این محصول که به عنوان ویتامین A دوتره (Deuterated Vitamin A) شناخته میشود، اصطلاحاً پاکتر از شکل طبیعی ویتامین A میسوزد. دوتریوم (Deuterium)، شکل بی خطری از هیدروژن است که بهطور طبیعی در بدن انسان تولید شده و غیر رادیواکتیو است. Alk-001 هماکنون در محله سوم کارآزمایی بالینی در بیماری اشتارگارت میباشد. . نام علمی Alk-001 عبارت است از C20-D3- retinyl . .acetate
شبکیه مصنوعی
جدیدترین تکنولوژی برای درمان بیماران شبکیه چشم، استفاده از شبکیه مصنوعی یا شبکیه الکترونیکی است. این تکنولوژی در سال ۲۰۱۶ ابداع شد، هرچند کیفیت تصویر بهدست آمده برای بیمارن چندان واضح نبود، اما پروژه شبکیه مصنوعی در حال ارتقا کیفیت است.
This disease is hereditary and therefore if there is a family history it is wise to be attentive, even though this does not mean that the disease is sure to manifest itself.
Approximately 90% of cases are transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner, i.e. both parents must have the affected gene and this is often very hard to establish. In this case, the possibility of a boy or girl having the disease is 25% and it should be remembered that 10% of cases, with a family history, are of dominant inheritance.As it is a recessive gene, the family history of the disease may not be known or available.
This is why it is necessary to pay special attention to the initial symptoms e.g. if children or adolescents find difficulty in reading or watching the television. At these ages, it is a good idea to explain the pathology to them so that they can be made aware of what will happen to them, can adapt to the situation and can lead a happy life.Stargardt’s disease causes out-of-focus vision that lacks sharpness. This makes it difficult to recognise faces and read both nearby and at a distance. As a result, colours with a similar shade (for example, red and green or blue and yellow) look alike.
A 40-year-old man experiencing decreased vision (visual acuity: 0.8) and dyschromatopsia in both eyes with Stargardt disease. A and B: The fundus photos of the right and left eyes respectively reveal the bull's eye maculopathy characterized by paracentral RPE depigmentation and atrophy, as well as pisiform, round, or dot-like yellow-white flecks. C and D: The red-free fundus images of the right and left eyes. E and F: OCT macula scans of the right and left eyes respectively, highlighting photoreceptor layer disorganization. (Courtesy of J. Khadamy) [5]
STARGARDT FINDINGS. (1A,1B) Fundus photography shows bilateral atrophic macular changes surrounded by diffuse pisciform flecks. (2A,2B) Fluorescein angiography reveals a dark choroid with hyperfluorescent pisciform flecks.[6]
A good knowledge of the disease helps sufferers to understand what is happening to them, adapt their lives to the new situation and take some recommended measures like using sunglasses with u/v protection and avoiding supplements that contain vitamin A.
In the field of research into treatments for this disease, science is progressing. The clinical trials and European projects in which the Barcelona Macula Foundation and the Institut de la Màcula participate in collaboration with leading international research centres are essential and lead to hope that the disease may be treatable in the future.[4]
Reference:
- fa.wikipedia.org/wiki/اشتارگات
- freedomscientific.com/visionloss/stargardt-disease
- lowvisionaids.org/stargardts-disease
- barcelonamaculafound.org/en/stargardts-disease-affects-young-people-who-must-face-up-to-a-new-way-of-life
- eyewiki.org/Stargardt_Disease/Fundus_Flavimaculatus
- aao.org/eyenet/article/diagnosis-management-of-stargardt-disease
See also:
- Stargardt macular dystrophy and therapeutic approaches
- What is the triad of Stargardt disease?
- What is Stargardt disease in children?

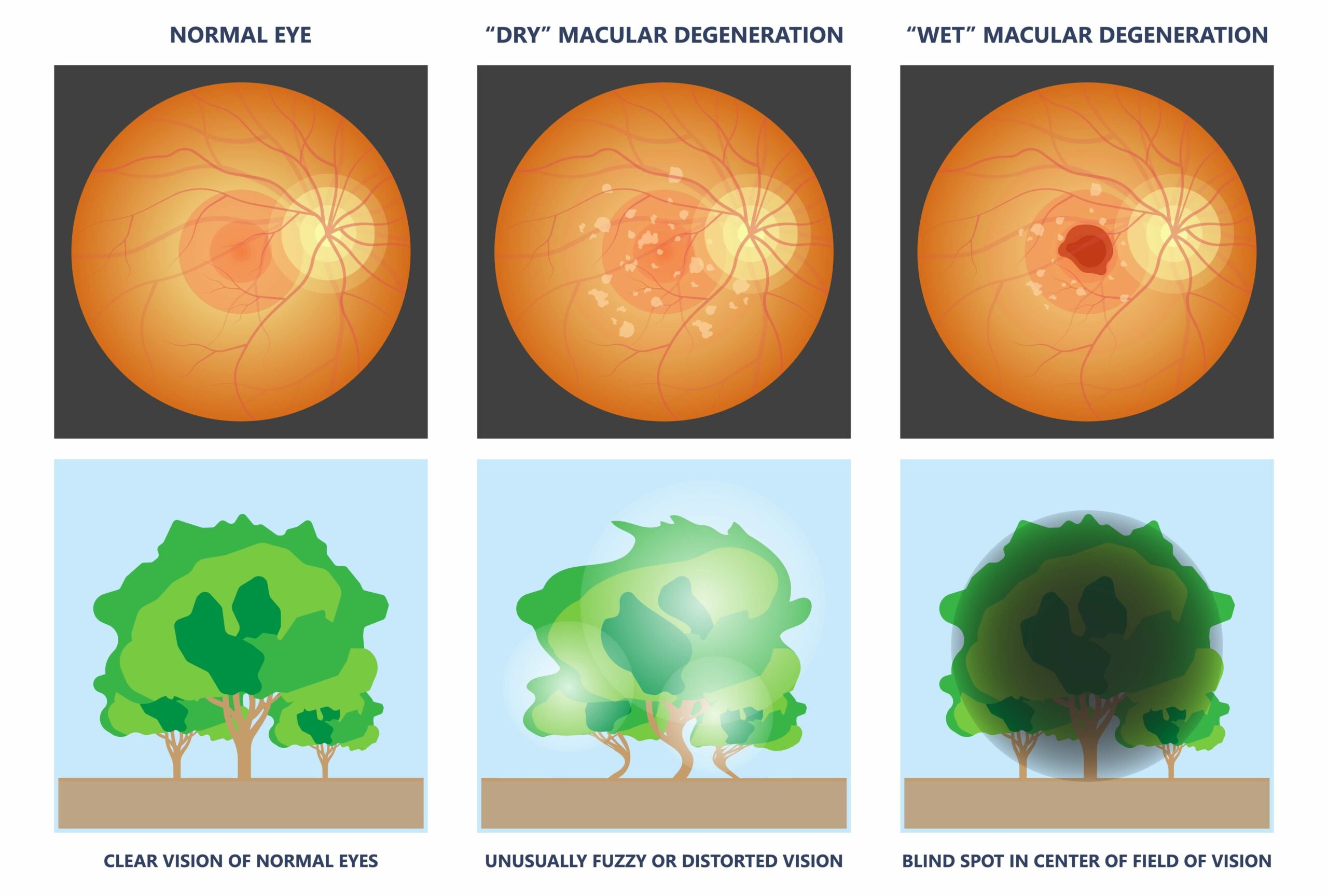



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Home-Remedies-and-Lifestyle-Changes-for-AMD_Illustrator_Michela-Buttignol_Final-afd2b2bd5d6743e5a473d4846f6573cd.jpg)








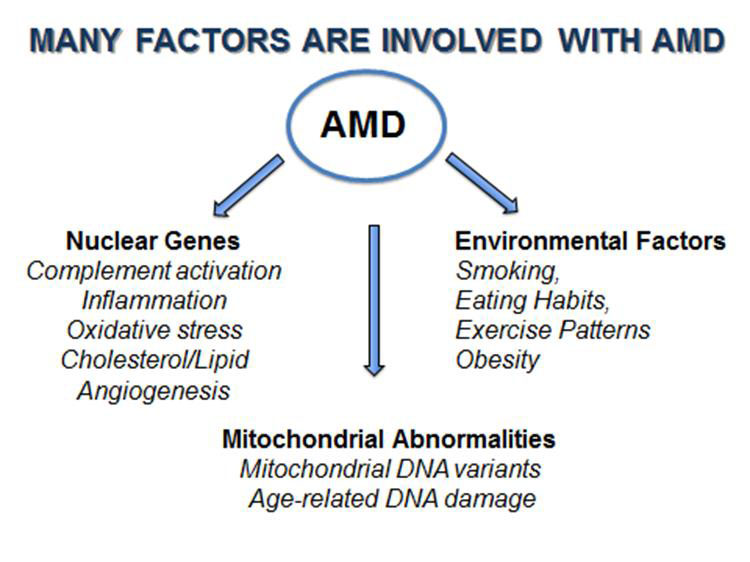
 Here are the most common causes and risk factors:
Here are the most common causes and risk factors:




 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.