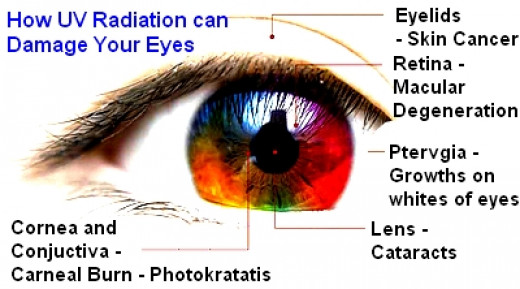
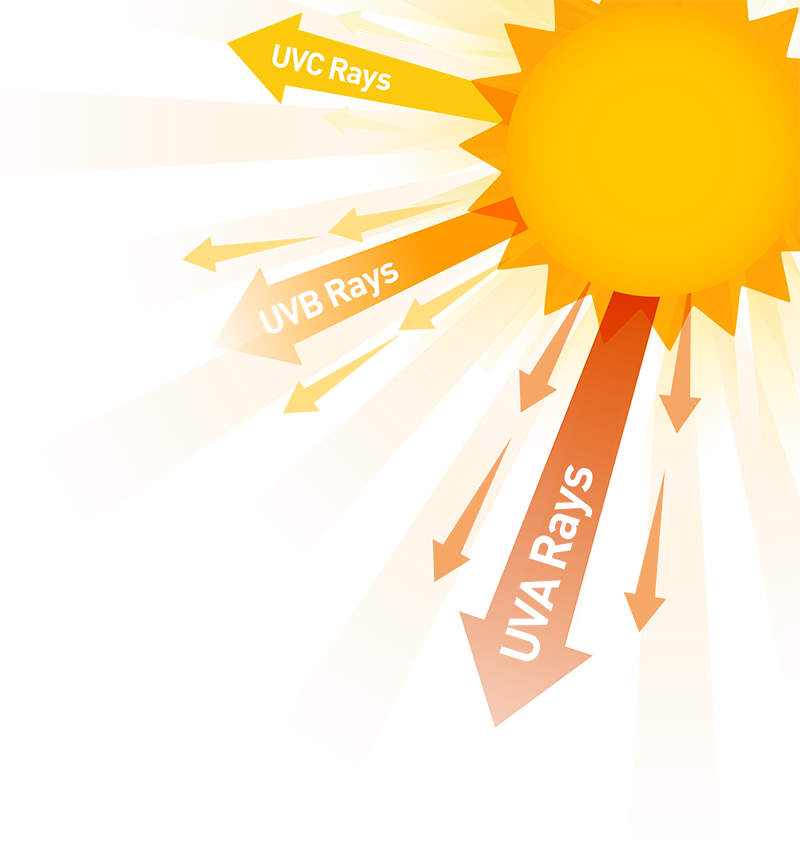
اشعه ماوراء بنفش یا همان (UV) دارای سه نوع طول موج UVA ،UVB و UVC است که اشعه «UVC» در لایه ازن جذب شده و به زمین نمیرسد و آن قسمتی که برای چشم مضر است UVB است که موجب سوختگی پوست و اثرات مضر روی چشم است.

مثلا وقتی UVB به روی برف تابیده میشود، میتواند موجب کوری برگشتپذیر شود و برای ۱۲ تا ۴۸ ساعت بینایی خود را از دست دهد.
دانشمندان بر این اعتقادند که تماس زیاد با اشعه UVB میتواند در مدت زیاد بیماریهای برگشتناپذیر، مانند: آب مروارید، تغییر در مرکز دید و ناخنک چشم را فراهم آورد.
اشعه «UVA» بیشتر توسط عدسی چشم جذب میشود و مدرکی برای ضرر چشم وجود ندارد. اشعهای که باید چشم را از آن مصون نگه داشت UVB است.
عینکها باید حداقل ۹۸ درصد از UVA و UVB را جذب کنند چون عینکی که استاندارد نیست، بسیار مضرتر از نزدنش است، چراکه عینک آفتابی باعث میشود مردمک چشم باز شود و حال اگر UV را جذب نکند، تمام اشعههای مضر به داخل چشم نفوذ میکنند.
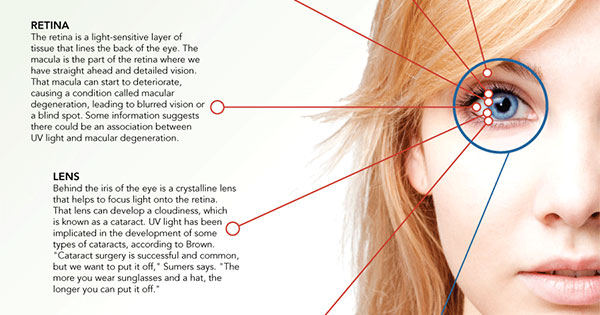
استفاده از عینکهای آفتابی به عنوان یک ضرورت و حفظ سلامت چشمها مطرح شده است . محافظت چشم در مقابل نور شدید آفتاب و اشعه فرابنفش موجود در آن بسیار مهم است. استفاده از عینک آفتابی مناسب در شرایطی که نور آفتاب شدید است، باعث بهتر شدن دید و پیشگیری از صدمه به عدسی و شبکیه چشم میشود. استفاده از عینکهای تقلبی نه تنها این خاصیت را ندارند بلکه سبب بسیاری از عوارض چشمیمیشوند که از آن جمله میتوان، کاهش بینایی، آب مروارید و بیماری شبکیه را نام برد.
در نور شدید، چشم احساس خستگی و کاهش دید رنگی میکند. در صورتی که چشمها بدون محافظ هر روز برای ساعات طولانی در نور آفتاب به سر برد احتمال ابتلا به آب مروارید بسیار افزایش مییابد.
توصیه های لازم در مورد انتخاب عینک آفتابی
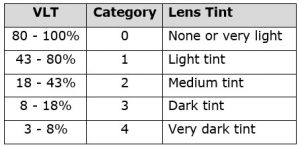
۱- افرادی که در حال اسکی کردن، حمام آفتاب گرفتن و کوهنوردی در ارتفاعات هستند باید حتماً از عینک آفتابی استفاده کنند. برای اینگونه محیطها عینکهایی لازمند که فقط ۱۲ ـ ۸ درصد نور را از خود عبور دهند.
۲ ـ عینکهای رنگی متمایل به سبز و قهوه ای به علت مختل کردن طیف رنگ ، مضر هستند . البته برای افرادی که میخواهند به مدت طولانی رانندگی کنند ، توصیه میشود از عینکهای قهوه ای استفاده کنند ، چرا که این عینکها نور آبی آسمان را کاهش وحدت بینایی را افزایش میدهند، لذا برای مصارف روزمره توصیه به استفاده از این رنگ نمیشود .
۳ -اگر پشت فرمان مینشینید توصیه میشود که از عینکهای آفتابی سبز رنگ استفاده نکنید چرا که تشخیص نور قرمز و زرد را مختل میکند و از این نظر مناسب نیستند. به عنوان یک اصل بدانید که بهترین رنگ برای عینکهای آفتابی در وهله اول خاکستری و پس از آن قهوه ای است.
۴ـ شیشههای عینک آفتابی باید مقاومت کافی داشته باشد. پلی کربنات از همه مواد مقاوم تر است.
۵ ـ قاب عینک باید بزرگ باشد تا محافظت کامل در این خصوص صورت گیرد .
۶ – یک عینک آفتابی استاندارد عینکی است که وقتی آن را در مقابل یک صفحه طرح دار تکان میدهیم نباید صفحه موجدار تار و کج و معوج دیده شود .
۷ – اگر میخواهید بدانید که تیرگی عینک آفتابی شما مناسب است یا نه، در یک اتاق با نور معمولی با عینک آفتابی به آینه نگاه کنید اگر عینک آفتابی شما مناسب باشد نباید چشمان خود را ببینید .
۸ – کودکانی که برای ساعتهای طولانی در زیر نور آفتاب در حال بازی کردن هستند باید از عینکهای مخصوص خودشان استفاده کنند .
۹ – اگر در محل کار خود با اشعههای زیاد در تماس هستید، عینک آفتابی جوابگو نخواهد بود لذا توصیه میشود عینکهای متفاوت و مخصوص استفاده نمایید (برای مثال در جوشکاری ویا کار با وسائلی که تولید اشعه میکند عینک ویا محافظ های خاصی لازم است )
۱۰ – افرادی که تحت عمل آب مروارید یا لیزیک یا لازک قرار گرفتهاند باید در مواجهه با آفتاب از عینکهای آفتابی مجاز استفاده کنند .
۱۱- بعضی داروهای پوستی یا چشمیحساسیت چشمها را به نور آفتاب بیشتر میکند در صورت استفاده از این داروها ( به عنوان مثال کسانی که از قطره های چشمییا قرص داکسی سیکلین استفاده میکنند ) باید حتماً از عینک آفتابی استفاده کنند .
۱۲- عینکهای آفتابی با شیشههای رفلکس که دارای پوشش آینهای هستند برای مصارف اسکی یا کوهنوردی مناسب میباشند .
۱۳- با توجه به هزینههای مختلف که روزمره متحمل میشوید خرید یک عینک آفتابی استاندارد نه تنها عملی درست و به جا بلکه ضروری میباشد . بهای استفاده از عینکهای تقلبی به خطر انداختن سلامتی چشم هایتان میباشد .
۱۴ – برای تهیه عینک آفتابی بهتر است با یک چشم پزشک مشورت کنید و یا از یک اپتومتریست کمک بگیرید . و جهت خرید آن به عینک فروشیهای معتبر مراجعه نمایید . با خرید یک عینک خوب به راحتی میتوانید تا چند سال از آن استفاده کنید .
۱۵- اگر دچار اختلال در بینایی هستید و از عینک طبی استفاده میکنید چنانچه مایل بودید میتوانید از عینکهای آفتابی مخصوص که بر روی عینک طبی قرار میگیرند استفاده نمایید و یا برای عینک طبی خود شیشه های فتوکروم و یا شیشه های رنگی سفارش دهید .

نحوه شناخت عینک استاندارد
«در لنز عینکهای ارزان مادهای به نام (Triace tate) است که فقط ۴۰ درصد ازUV را جذب میکند و برای چشم بسیار مضر هستند بنابراین بهترین راه شناخت عینکهای استاندارد، استفاده از دستگاه UV متر است که اغلب در عینکفروشیهای معتبر یافت میشود.»
بدون استفاده از دستگاه «یووی متر» جهت شناخت استاندارد بودن عینکهای آفتابی، تشخیص یک عینک آفتابی مناسب، حتی برای چشم پزشکان نیز سخت و غیرممکن خواهد بود.
گفتنی است این دستگاه باید UV عینک را از ۹۸درصد به بالا نشان دهد. همچنین گاهی علامت «۴۰۰ UV» در کنار برخی از عینکها درج شده است که نشاندهنده قابلیت حفاظت بر علیه UVB است.
نمیتوان هر عینک گرانقیمتی را استاندارد قلمداد کرد و باید تمامی آنها توسط دستگاه (یوویمتر) تست شوند.

خاصیت عینکهای شیشهای بدون نمره
در حال حاضر اکثر عینکهای طبی و آفتابی بهدلیل هزینههای بالای آن از شیشهای تبدیل به تلق شدهاند، ولی جالب است که بدانید اگر شیشه بدون شمارهای را جلوی چشمان خود بگذارید، باعث میشود ۹۸ درصد از UV توسط آن جذب شود. آنچه در انتخاب عینک آفتابی مهم میباشد، این است که باید کل چشم توسط آن گرفته شود، بنابراین استفاده از عینکهای کوچک که بیشتر برای زیبایی طراحی شدهاند و هیچ پوششی ندارند، توصیه نمیشود.
آیا کودکان هم به عینک آفتابی نیاز دارند ؟
کودکان به دلیل این که ممکن است بیش از سایرین در معرض آفتاب قرار گیرند، احتیاج به عینکهای آفتابی دارند. هر قدر افراد جوانتر باشند UV بیشتر به چشم آنها صدمه خواهد زد، چرا که قرنیه و عدسی چشم کودکان بسیار شفاف است وUV بدون برگشت داخل چشم میرود در صورتی که در افراد سن بالاتر به دلیل کدر بودن عدسی و قرنیه، مقداری ازUV بازتاب خواهد داشت، پس بهتر است کودکان و بزرگسالان در معرض آفتاب از ۱۰ صبح تا ساعت۱۴ زدن عینک را به هیچ وجه فراموش نکنند؛ چرا که در این مدت زمان، حتی اگر شخص در سایه نیز قرار داشته باشد، خطر صدمه اشعهUV چشمان را تهدید میکند.


فیلتر پلاریزه
اغلب اشعههای مضر از استوا میآیند و بهشکل افقیاند. عینکهای پلاریزه میتوانند جلوی این اشعهها را به خوبی بگیرند، چرا که این عینکها اجازه میدهند فقط اشعههای عمودی، داخل چشم شوند و تنها مشکل این عینکها این است که اگر خودرویتان (السیدی) دارد شما به هنگام نگاه کردن به این صفحه، کمی دچار مشکل شده و ممکن است این صفحه را واضح نبینید. بنابراین، این نوع از عینکها بیشتر برای افرادی که دارای دید بسیار خوب و شغل خلبانی یا تیراندازی هستند توصیه میشود.
آیا رنگ رنگ شیشه عینک هم مهم است ؟
رنگ و لایههای مختلف موجود در شیشه هریک با توجه به کاربرد آن طراحی میشود مثلا رنگ خاکستری به دلیل این که شدت نور را در تمامی رنگها به طور یکسان کم میکنند و کمترین اختلالی را در دید رنگی ایجاد میکنند، برای رانندگی و سایر کاربردهای روزمره مناسبند. دکتر اساسی درخصوص عینکهای شیشه زرد میافزاید: این عینکها نور آبی را تا حد زیادی جذب میکنند، بنابراین بیشتر سطحها میتوانند آن را منعکس و منتشر کنند و به همین دلیل عینکهای اسکی بیشتر زرد هستند.
همچنین عینکهای قهوهای علاوه بر جذب بهتر نور آبی و فرکانسهای بالا، اشعه ماوراءبنفش را هم بیشتر جذب میکنند و عینکهای سبز بخشی از نور آبی را فیلتر کرده و درخشندگی سطوح را کاهش میدهد و در پایان عینکهای قرمز و ارغوانی که بیشتر برای شکار و اسکی روی آب مناسبند در محیطهای سبز و آبی استفاده میشود.

آیا در زمستان هم احتیاج به عینک آفتابی داریم ؟
استفاده از عینک آفتابی در زمستان، بخصوص در برف را توصیه می شود . از آنجا که برف بازتاب ۸۰ درصد ازUV را دارد و زمین و آب فقط ۱۰ درصد ازUV را منعکس میکنند، اهمیت استفاده از عینک آفتابی در زمستان کمتر از استفاده از آن در فصل تابستان نیست.
عیـنـک آفتابی خوب باید شرایط زیر را داشته باشد :
۱- چشمان شما را در برابر اشعه ماوراء بنـقش محافظت کند.
۲- چشمان شما را در برابر نور شدید خورشید محافـظت کند.
۳- چـشمـان شما در برابر نورهای زننده و خـیـره کـنـنـده محافظت کند.
۴- وضوح و کنتراست را بهبود ببخشد.
یـک عیـنـک ارزان قیـمت و بی کیفیت مـعمـولا مـزایای فـوق را در اختیار شما قرار نمی دهـند بـلکه تنها از شدت نور میکاهد ولی اشعه ماوراء بنفش را حذف نمی کنـد. از ایـن رو عـنـبـیــه چـشمـان بـواسطـه کـاهش شـدت نـور منبسط تـر و بازتر شده و اجازه می دهد اشـعـه مـاوراء بنـفـش بیـشتری به آنها برسد که سبب آسیب به شبکیه چشم و در پی آن ابتلا به آب مروارید و حتی سرطان چشم می گردد. بنـابـرایـن حتما از عیـنـک هـای آفـتـابی دارای حداقل حفاظت UV-400 بـا مـارک هـای مـعـتبر استفاده کنید.
انواع جنس فریم عینک های آفتابی
۱- پلاستیکی
* CELLULOSE ACETATE – ZYL: مقرون به صرفه و خیلی سبک میباشد.
* PROPIONATE: پـلاسـتـیـک نـایـلونی که حساسـیـت زا نمیباشد و سبک وزن است.
* NYLON – GLIDAMIDE: گلیدامید مقـاوم در بـرابر گـرما و سـرمـا بــوده و انـعــطاف پذیر اما سخت و حساسـیـــت زا نمیباشد. فریم های پلاستیکی شکننده تر از فریم های فلزی بوده و در برابر تابش خورشید بمرور استحکامشان کاهش می یابد.
۲- فلزی
* MONEL: آلیاژی از چند فلز میباشد. ضد خـوردگی بوده و معمولا دارای روکش پالادیوم است.
* TITANUM: سبک و بادوام، با استحکام و مقاوم دربرابر خوردگی (نقره ای رنگ میباشد)
* BERYLLIUM: ارزان قیمـت، مـقـاوم در برابر خوردگی و کدر شدن، بسیار قابل انعطاف(خاکستری مات)
* STAINLESS STEEL: اسـتـیـل ضـد زنـگ سـبـک وزن و حساسیت زا نمی بـاشد، مـقـاوم در بـرابـر خــوردگــی و ساییدگی بواسطه داشتن فلز کرمیوم در ترکیبش
* FLEXON: نـوعـی آلـیـاژ تـیـتـانیـوم مـــی بـاشـد که بـه “فلز حافظه” موسوم است چون در صـورت آسـیـب دیـدن مـجـددا بـه شـکـل اولیه خود باز می گردد. حـتـی پـس از پیچاندن خم کردن و له کردن. سبک وزن، ضـد خـوردگی و حساسیت زا نمیباشد.
* ALUMINUM: سبک، بسـیـار مـقاوم در برابر خوردگی، برای استحام بیشتر با آهن و سیلیکون ترکیب میگردد. فریـم باید هم اندازه و مکمل شکل و رنگ پوست شما باشد. مـثـلا افـراد بـا صـورت گـرد بهتر است فریمهای مستطیل شکل را انتخاب کنند و افـرادی که فرم صورتشان مربعی و مستطیلی شکل است بهتر است فریمهای بیضی شکل را انتخاب کنند. نکته دیگر آنکه سطح بالای فریم نباید ابروهای شما را بپوشاند.
انواع فریم، جنس لنز…
انواع فریم
۱- WRAP-AROUND: به فریمهایی اطلاق میگردد که از قوس صورت تبعیت کرده و چشمها را کاملا میپوشاند. در مقابل برف و باد و باران نیز محافظند.
۲- CLIP-ON: به فریمهایی اطلاق میگردند که مستقیما روی عینکهای طبی قرار میگیرند.
جنس لنز (عدسی) eResearch by Navid Ajamin --- Winter 2012
۱- CR-39: نـوع پلاستیکی کـه از یـک نـوع رزیـن سـاخته میشود
۲- POLYCARBONATE: پلاستیک مصنوعی بسیار سبک وزن و دارای استحکام زیاد میباشد.
۳- ACRYLIC: لـنـزهـای آکــریلی ارزان قـیـمـت و سـخـت میباشد اما وضوحشان کمتر از پلی کربنات میباشد. ولی زود خراشیده میشوند.
۴- شیشه: سنگین وزنتر از لنزهای پلاستیکی بوده اما در برابر خراشیدگی مقاومت بیشتری دارند. خطر شکستن.
* لنزهای پلاستیکی سبکتر بوده و در برابر ضربه مقاومت بیشتری دارند.
* لنزهای قابل تعویض لنزهایی می بـاشنـد کـه دارای تـه رنـگهای متـفــاوت بوده و روی فریمهای ویژه قابل جایگزینی با یکدیگر میباشند.
چرا بعضی از لنزها از لنزهای دیگر تیره تر است ؟
میزان تیرگی لنز بستگی به محیطی دارد که می خواهـیـد از عیـنـک استـفـاده کنید. در محیطهایی که شدت نور شدید است مانند ورزش کـوهنـوردی و اسکی روی برف، شما نیاز به لنزی دارید که بیشتر نور را سد کند %۹۵ برای رانندگی و کنار دریا %۹۰-۷۰ نـــور را جذب کند و لنزهایی که %۲۰-۱۰ نور را کاهش میدهد صرفا برای نـمایـش مد و خوش نمایی مناسب میباشد. نکته مهم این است که میزان تیرگی لنز هیچ ارتباطی با میزان حفاظت کنندگی آن عینک در برابر اشعه ماوراء بنفش ندارد. رنگ ها لنز و کاربرد آنها، پوششهای لنز…
ته رنگ لنز
لنزهـا در تـه رنـگای متـفـاوتی مـوجود می باشند که هر کدام برای فعالیت های ویژه ای مناسب است.
۱- ته رنگ خاکستری: یک ته رنگ فوق العاده که سبـب کـاهش کـلـی روشنـایــی نور گشته و چشمها را در برابر تابشهای زننده (خیره کننده) محافظت کرده و بـرای رانندگی و استفاده عمومی مناسب میباشد.
۲- ته رنگ زرد و طلایی: میزان نور آبی را کاهش داده و در عـیـن حـال به فرکانسهای دیگر نور اجازه عبور می دهـد. تـه رنـگ زرد بـطور کـلی رنـگ آبـی را حـذف کرده و سبب میگردد همه چیز واضح تر بنظر برسد (چـون نور آبی تمایل به پخش و بازتاب فراوان دارد از این رو حذف آن در وضوح دید موثر است) و به همین خـاطر اسـت کـه بیشتر عینکهای ویژه اسکی روی برف زرد رنگ میباشند. در واقع این ته رنگ دید نور را مختل میکند برای رانندگی در شب، هوای ابری و مه آلود نیز مناسب است.
۳- ته رنگ قهوه ای و کهربایی: ته رنگهای عمومی میباشند و مزایای آن کاهش نور زننده و حذف فرکانسهای بالای نور مانند نـور آبـی و مـاوراء بنـفش را دارد. مانند ته رنگ زرد دید نور را مختل میکند اما کنتراست و وضوح را افزایش میدهد. برای دویدن، دوچرخه سواری و رانندگی مناسب است.
۴- ته رنگ سبز: کاهش نور زننده و حـذف نـور آبی از ویژگیهای آن میـباشد از آن رو که ته رنگ سبز بالاترین میزان کنتراست و بیشترین درجه تیزبینی را فراهم می آورد بسیار محبوب میباشد.
۵- ته رنگ صورتی و قرمز: کنتراست عالی را از اجسام بـا پـس زمیـنـه آبـی و سـبـز فراهم می آورد. برای شکار و اسکی روی آبی مناسب است.
۶- ته رنگ آبی: بیشترین نور آبی را از خود عبور می دهند. بـرای گـلف و تـنـیـس و یـا نشانه گیری به سوی هدفهای سبز رنگ.
پوشش های لنز
۱- ultraviolet: این پوشش اشعه ماوراء بنفش را بلوکه می کند. حـتــما هنگام خرید عـیـــنکی را انتخاب کنید که تا امواج ۴۰۰ نانومتر را حذف کرده و ۱۰۰ درصد امـواج مـاوراء بنفش را بلوکه کند. برخی از عینکهای آفتابی اشعه مادون قرمز را نیز حذف میکنند.
۲- scratch-resistant: ضـد خـش بــروی پلاستیکها اعمال می گـردد چـون لـنـزهـای شیشه ای خودشان تقریبا ضد خش می باشند.
۳- photochromic: لنزهای فتو کرومیک هنگامیکـه در معرض نور خورشید قرار میگیرند تیره می شوند. پوشش این لنـزهـا از تـرکیـبـات نـقره مـانـنـد کـلرید نـقـره و هـالـید نقره میباشد. توجه داشته باشید که فتوکرومیکها به نور مرئی واکنش نسان نمیدهند و تنها هنگامی که در معرض اشعه ماوراء بنفش واقع میگردند تیره میشوند از ایـن رو در داخـل اتومبیل بخاطر آنکه شیشه اتومبیل اشعه ماوراء بنفش را اجازه عبور به آن نمی دهـــد، بنابراین لنز فتوکرومیک تیره نمی شود. زمانی که نیاز است تا لنز تیره گردد گاهی اوقات به ۸ دقیقه میرسد.
۴- flash یا mirroring: ایـن پـوششها لنز را مـانـند آینه کرده و ۱۰ الی ۶۰ درصد بیشتر نور را کاهش داده و جذب میکند. میتواند از نقره -طلا و یا مس باشد. در ارتفاعات و برای برف وشن وآب مناسب است.
۵- ar یا anti-reflective: پوشـشـی اسـت کـه ضـریب شــکسـتــی مــابـــیـن هـوا و شـیـشـه داشـتـه و شدت نـور بـاز تـابیده از سطح داخلی و خارجی لنز یکسان میگردد. در واقــع این پوشش سبب میگـردد نـور بـیـشـتـری بــه چـشمـها رسیـده در عـیــن حال که نور زننده را بسـیار کاهش میدهـد و هــمچنین چشمـان شمـا نـمایـان تـر می گردد. بسیار مناسب برای رانندگی در شب.
۶- polarization: امـواج نــور خــورشـیـد و یـا مـنابع نور مصنوعی مـانند لامپ ارتعاش یافـتـه و در تـمـام جـهـات پخش می گـردد. در ایـن پـوششـها از مــواد استفاده شده که به طـور طـبـیـعی در یـک پـیـوند مـوازی در بـرابر هم ردیف شده اند. زمانی که نور به لنـز می تـابـد مانند یک فیلتر میکروسکوپی عمل کرده و امواج نوری را که با ردیفهای مـوازی مطابقت داشته را جذب کرده و به مابقی اجــــازه عـــبور میدهد. بیـشتـرین نـور زننده از سـطـوح افـقی حاصل می گردند بنابراین این لنزها طوری تنظیم می شــونـد کـه امــواج انعکاسهای یافته افقی را حذف میکنند و بـه شـمـا اجازه میدهد به سطوحی مانند آب، یخ و برف نگاه کنید...
Reference: pezeshk.us
























 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.