Dimness of vision may be noted due to muted color vision or gray areas.
This is a symptom of a variety of conditions, including amblyopia, optic neuritis, retinal detachment, macular degeneration, glaucoma, cataracts, or brain tumor.

- dimness /dˈɪmnəs/
What is the meaning of dimness of light?
lacking in light; not bright or harsh. “a dim light beside the bed” synonyms: subdued. dark. devoid of or deficient in light or brightness; shadowed or black.

What is a word for dimness?
dimness: blackness، dark، duskiness، gloom، murk، murkiness، shade.
What does dimness mean?
dimness noun [U] (NOT CLEAR)
the quality of not having or giving much light: The light bulb formed a bright spot in the dimness of the barn. The dimness of the weak candle hid the little blemishes on her face.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dimness-of-vision-5210447_final-77846d51f16544fb9b5117144a1f9798.jpg)
Why is my vision bad in dim light?
The tissues that make up the forward parts of your eyes need to be clear so light can pass through them. When they aren't clear or don't allow light to pass through them correctly, it limits how much light reaches your retinas and can cause difficulties seeing in dim light.
There is currently no evidence at all to suggest that reading in poor light damages your eyes. However, one thing is clear: reading by light requires more strain on the eyes to make out the words. This makes reading more strenuous, and the eyes get tired more quickly, potentially resulting in red eyes and headaches.

What is Pelli Robson?
Pelli-Robson test measures contrast sensitivity using a single large letter size (20/60 optotype), with contrast varying across groups of letters. Specifically, the chart uses letters (6 per line), arranged in groups whose contrast varies from high to low.
A Pelli-Robson score of 2.0 indicates normal contrast sensitivity of 100 percent. Scores less than 2.0 signify poorer contrast sensitivity. Pelli-Robson contrast sensitivity score of less than 1.5 is consistent with visual impairment and a score of less than 1.0 represents in visual disability.
Who invented the Pelli Robson chart?
Developed by Dr D Pelli of Syracuse University, New York and Dr J Robson of University of Cambridge, England. The Pelli-Robson chart utilises letters of the same size but with reducing contrast to provide a quick means of assessing patient contrast sensitivity thresholds.
Winter is probably the best time to get round to reading a good book, especially by candlelight or the soft light of a bedside lamp. Children even like to hide under the covers with a pocket lamp. However, the joy of burying oneself in a book is often tempered by the fear that doing so might damage our eyes. Almost everyone's been told it at one time or another: "Put the light on, you'll damage your eyes!" But there's no need to worry – reading in the dark doesn't damage your eyes at all. However, if you need reading glasses, you should wear them.
What's the difference between Pelli Robson and Snellen?
Answer: Similar to the Snellen test, the Pelli-Robson test is where the optician asks you to identify the letters on a chart. Unlike the Snellen test, this uses printed letters of decreasing contrast, with three letters at each contrast level. It's designed to identify patients with poor sensitivity to contrast.

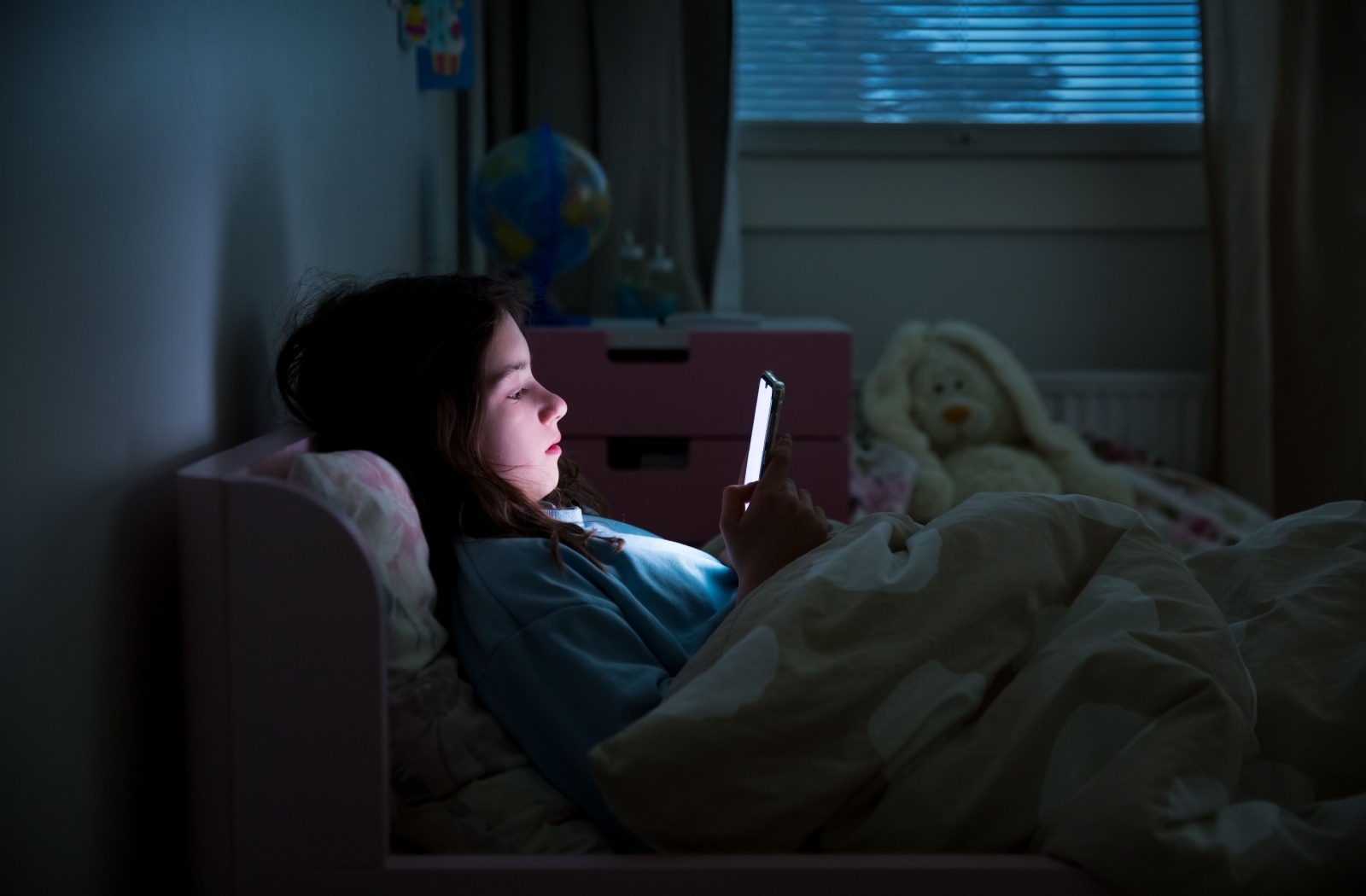
Knowing that smartphone use in the dark can damage your retina, it's important to take the proper precautions to protect your vision. Here are some ways to do this. It may sound difficult to give up time on your smartphone, but doing so can help you sleep better, avoid health problems and preserve your vision.
Mobile phones emit high-energy blue light, which can penetrate deep into the eye and potentially cause damage to the retina over time. Prolonged exposure to blue light, especially before bedtime, may disrupt sleep patterns by suppressing melatonin production, leading to insomnia and other sleep-related issues.


Scientists still argue about this issue today: reading in poor light damages your eyes. But there's no reason to be concerned. There is currently no evidence at all to suggest that reading in poor light damages your eyes. However, one thing is clear: reading by light requires more strain on the eyes to make out the words. This makes reading more strenuous, and the eyes get tired more quickly, potentially resulting in red eyes and headaches. Despite this, the eyes themselves do not suffer from this process, according to a study by American scientists published in the renowned periodical British Medical Journal. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- winter 2025

Why does reading in low light cause eye strain?
In dark or low light, it is harder for your eyes to focus. You also tend to blink less which can lead to dry eyes and eye strain. Despite this, difficulty seeing in the dark could be a sign of certain eye conditions. Your eyesight deteriorates as you get older which can sometimes make it more difficult to see at night. This condition is known as presbyopia. Also, myopia (or near-sightedness) and astigmatism can make reading in low lighting more tricky.

Will reading in bad light ruin your eyesight?
As children, many of us were warned not to read in low light - for example, under our bedcovers with a flashlight - because it would damage our eyesight in the long term.
No As children, many of us were warned not to read in low light - for example, under our bedcovers with a flashlight - because it would damage our eyesight in the long term.
This belief is so widely accepted that even some health care professionals do not question it. But this idea is nothing more than a medical myth, and there is no strong evidence to support it.

Reference:
- visionaid.co.uk/eye-conditions--cataracts
- verywellhealth.com/dimness-of-vision-5210447
- vectorvision.com/contrast-sensitivity-background
- marsperceptrix.com/mars-contrast-sensitivity-tests
- specsavers.ie/help-and-faqs/what-is-the-pelli-robson-test
- veatchinstruments.com/Pelli-Robson-Contrast-Letter-Test-Chart
- oldsouthoptometry.com/can-screen-time-affect-my-childs-vision
- glassesdirect.co.uk/blog/is-reading-in-the-dark-bad-for-your-eyes
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10118-night-blindness-nyctalopia
- researchgate.net/figure/The-Pelli-Robson-Chart-after-Denis-Pelli_fig2_355393888
- moorfields.nhs.uk/about-us/news-and-blogs/blogs/the-potential-impact-of-your-mobile
- brainzooming.com/blog/is-your-organizational-vision-dimmed-and-you-dont-even-know-it
- scmp.com/lifestyle/family-education/article/1386761/hits-and-myths-will-reading-bad-light-ruin-your-eyesight
- healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/2021/11/can-reading-low-light-harm-your-eyes-top-10-eye-health-myths-debunked
- zeiss.com/vision-care/en/eye-health-and-care/health-prevention/does-reading-in-poor-light-damage-your-eyes.html
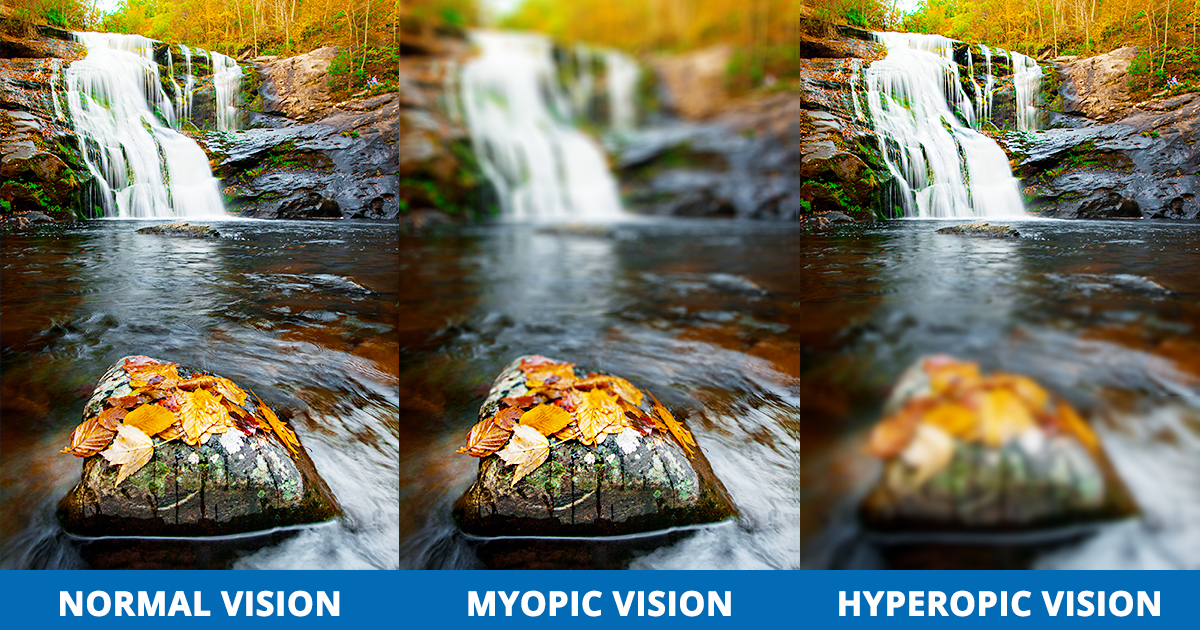
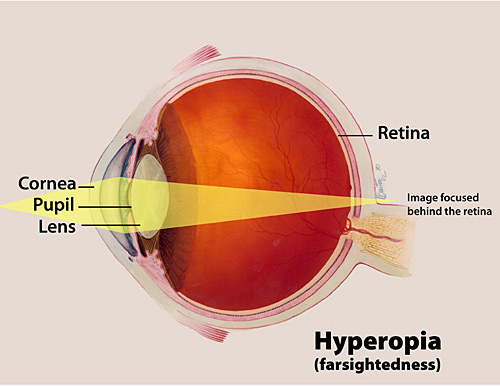


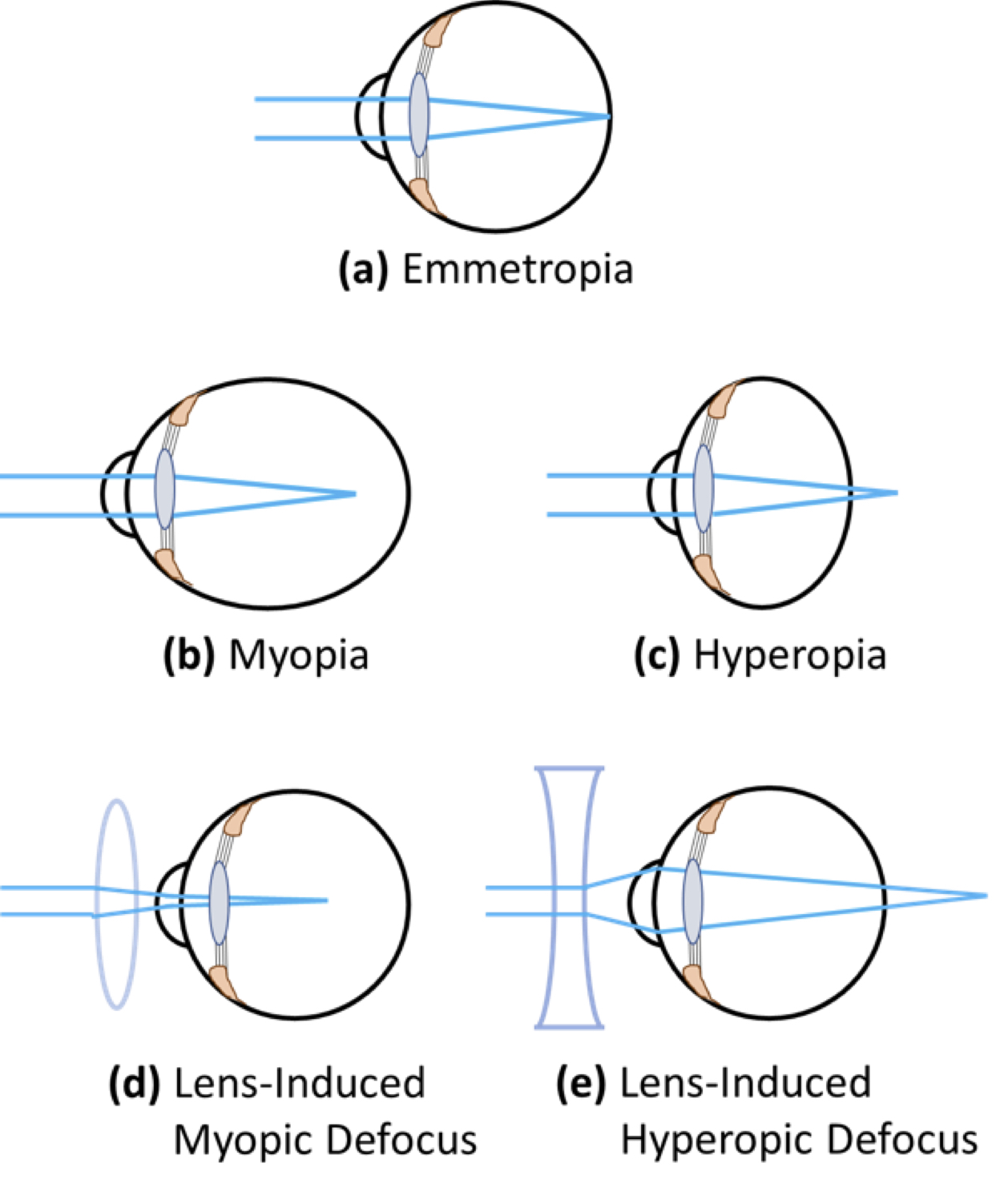
 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.