Blue light, which is part of the visible light spectrum, reaches deeper into your eye and its cumulative effect can cause damage to your retina and it is connected to the development of age-related macular degeneration. Blue light is not just entering your eye from natural sources like the sun. Sunlight is the main source of blue light, and exposure outdoors during daylight is the main source for most people.

Blue light lenses have become increasingly popular in our digital age. While there’s no proof they protect against certain eye conditions, there are well-documented benefits, particularly in regulating our sleep-wake cycle.
Hormone Regulation
Exposure to blue light, particularly during the evening, has been shown to disrupt melatonin production, the hormone responsible for regulating our sleep-wake cycle. This disruption can lead to difficulties falling asleep and achieving restful sleep.
Blue light lenses can help mitigate the impact of blue light by limiting how much reaches your eyes, supporting the natural release of melatonin and promoting a more restful and rejuvenating sleep.
There are also many man-made, indoor sources of blue light, including fluorescent and LED lighting, and flat-screen televisions. The display screens of computers, electronic notebooks, smartphones, and other digital devices emit significant amounts of blue light, although it is only a fraction of the amount of blue light emitted by the sun. In a laboratory,sources of blue light are blue LED arrays and intense white light sources (projection lamps, floodlights, microscope lights,welding arcs, etc.).The most common type of LED used in electronic devices is a white-light LED, which actually has a peak emission in the blue wavelength range (400 – 490 nm).

Depression & Anxiety Management
Research has consistently indicated a connection between disrupted sleep and susceptibility to depression and anxiety. Blue light lenses can effectively regulate our sleep-wake cycle and indirectly support mental health. These lenses promote healthier sleep patterns and overall well-being. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- winter 2017
Blue light lenses may contribute to improved hormone regulation and alertness and provide benefits for managing depression and anxiety.
But blue light lenses are not only helpful for those who spend time in front of digital devices—they can also be beneficial for outdoor use, such as when engaging in activities in direct sunlight. These lenses help reduce glare and make it easier to focus on your activity or enjoy the scenery around you.
Always consult an eye care professional for personalized advice and recommendations regarding your eye health needs.


During daylight, blue wavelengths of light can be beneficial, playing an important role in setting circadian rhythms, boosting attention and mood. But we didn’t evolve to be exposed to it as much as we are. In addition to the ample blue light in sunlight, most of the light we are exposed to via digital devices is also blue.
For example,Moreover, the eye’s cornea and lens are unable to block or reflect blue light.
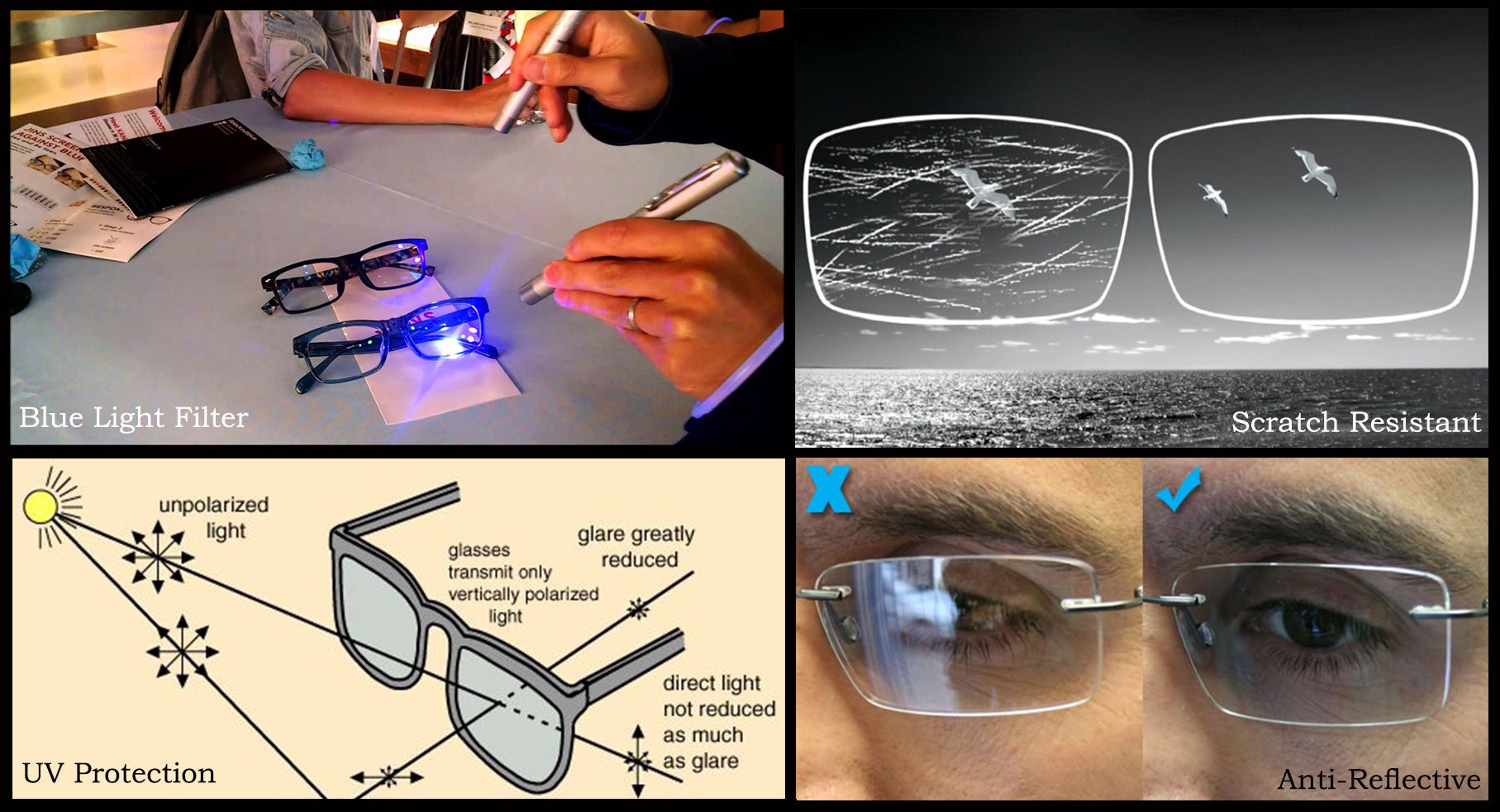
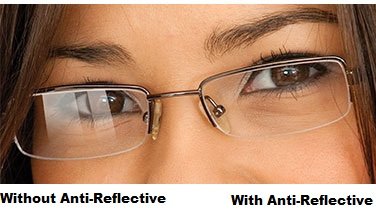
If you have presbyopia and routinely wear bifocals or progressive lenses, prescription computer glasses give you the additional benefit of a much larger field of view for seeing your entire computer screen clearly. (Keep in mind, though, that this type of computer eyewear is exclusively for seeing objects within arm's length and cannot be worn for driving or other distance vision needs.) Also, a number of lens manufacturers have introduced special glare-reducing anti-reflective coatings that also block blue light from both natural sunlight and digital devices.
Advice when using smartphones and tablets

- Set your device to auto brightness.
- Hold your tablet or smartphone at arm’s length (or about 70cm) from your eyes.
- Make the font bigger to stop strain on the eyes.
- Only use the device for a couple of hours a day in one sitting.Then take a break and come back to it later.
In addition:
- Have your eyes tested regularly and take regular breaks from your computer and hand held device.
- Use good sunglasses with a UV filter when outside.
- Have a healthy and varied diet rich in Vitamin A, lutein, zeaxanthin and mesozeaxanthin which comes from spinach and peppers which will protect the eyes.
Key Points About Blue Light
- Blue light is everywhere.
- HEV light rays make the sky look blue.
- The eye is not very good at blocking blue light.
- Blue light exposure may increase the risk of macular degeneration.
- Blue light contributes to digital eye strain.
- Blue light protection may be even more important after cataract surgery.
- Not all blue light is bad.
- “Health clock” hormones like melatonin are controlled by your body’s exposure to blue light.
Damaging effects of blue light
Too much light in the ultraviolet and blue-violet bands can damage the human eye.
As well as leading to painful inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea, it can also cause damage to the eye's crystalline lens (e.g. cataracts) and especially to the retina (macular degeneration).
That's why it is so important to wear sunglasses with 100% UV protection in strong sunshine, especially in situations where there is a lot of glare such as on water or snowy mountain
slopes.
According to Harvard researchers, exposure to blue light at night “throws the body’s biological clock—the circadian rhythm—out of whack” and may contribute to an increase of sleeping disorders, blood sugar, hunger, depression, cancer,diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Blue light during the day helps us feel awake and sets our bodies’ schedule to fall asleep at night, which is critical for migraine sufferers.
All digital devices with viewing screens emit significant amounts of blue light (also called "high-energy visible light" or "HEV light") which might increase a child's risk of macular degeneration later in life.
Blue light glasses were first invented in the 1960s to assist with this growing issue but became popular beginning in the early 2000s. They work by blocking a percentage of blue light with a special coating on the lenses that reflect it away from your eyes.
Founded in Chicago in 1986, BluBlocker Sunglasses made history with a revolutionary lens that reduced brightness while increasing contrast and visibility, using the same groundbreaking technology originally developed for NASA to block harmful UV rays and blue light during space travel.
BlockBlueLight was founded by Daniel Ebbett in 2016, born out of his personal struggle with chronic insomnia and migraines.
What are Z-blue lenses?
Z1 lenses: Z-Blue™ is used for persons who are sensitive to flashing lights and repeating patterns. This lens cuts down on wavelengths from 580-640nm, they reduce the amount of light and filter out red light.






Though the sun emits significantly more HEV light than computers and other digital devices, the added exposure to blue light kids receive from these devices and how close these electronic screens are to a child's eyes for hours each day have many eye care providers worried about potential eye damage over time.

And many eye care practitioners who specialize in children's vision believe prolonged computer use among children puts them at risk for progressive myopia.
Kids and computers are nearly inseparable these days. With many school-age kids and even preschoolers spending hours in front of a computer every day, it's worth considering what effects computers might have on your children's eyes and their vision. When you work at a computer for any length of time, it's common to experience eye strain, blurred vision, red eyes and other symptoms of computer vision syndrome(CVS). This is because the visual demands of computer work are unlike those associated with most other activities.
To reduce the risk of focusing fatigue that can cause advancing nearsightedness among kids who spend a lot of time on a computer, many eye doctors recommend frequent breaks from computer work. Some call this the "20-20-10" rule: Every 20 minutes your child should take
his eyes off the computer and look at an object at least 20 feet away for at least 10 seconds.
Blue Control lenses reduces the symptoms of digital eyestrain such as dry eyes, sticky eyes, and the feeling of grittiness or "sand" in the eye. Protect your lenses against water, dirt, grease and dust, keeping them clean for longer!
The following symptoms are characteristic of someone who uses the computer/phoneset/tablet for a very long period of time:
- Dry eyes
- Red eyes
- Eyestrain
- Backache
- Headaches
- Visual Fatigue
- Light sensitivity
- Lower self-esteem
- Weight gain or loss
- Progressive myopia
- Disturbances in sleep
- Premature presbyopia
- Loss of cognitive ability
- Neck and shoulder pain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Burning or stinging eyes
- Impaired socialising skills
- Leads to screen addiction
- Weakened emotional judgment
- Delayed learning in young children
- Blurred or strained vision/double vision
- Lack of concentration and focus of mind
- Susceptibility to chronic health conditions

Which is better blue cut or blue control?
The choice between Blue Cut and Blue Control lenses depends on your specific needs and lifestyle: For Heavy Screen Users: If you spend long hours in front of digital screens, Blue Cut lenses might be the better choice due to their strong blue light blocking capabilities.
Continuous exposure to blue light after sundown can disturb the sleep-wake cycle and make it difficult to fall asleep in the long run. Tinted lenses mimic the conditions of nature by blocking all artificial blue light and regulating a normal sleep-wake cycle, thus promoting good eye-health and sleep.
Is it okay to buy cheap blue light glasses?

Cheap blue light glasses don't target the complete range.
For all we know, the lenses could be ineffective at shielding your eyes from the peak wavelengths.
Reference:
healthrising.org healthline.com health.clevelandclinic.org migrainekey.com ap.lbl.gov/ehs/safety forbes.com/sites/fionamcmillan gundrymd.com/blue-light-warning activesgcircle.gov.sg/activehealth riverheightseyecare.com/what-are-the-benefits-of-blue-light-glasses eyekit.co eyeacademy.com allaboutvision.com reviewofoptometry.com crew.co/blog psychguides.com zeiss.com blockbluelight.com health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/blue-light-has-a-dark-side
See also:
- Does blue light keep you awake at night?
- How Blue Light Effects Your Eyes and Brain
- Is it bad for your eyes to watch TV too close?
- Is dark mode better or worse for your eyes?
- Is it bad for your eyes to watch TV in the dark?
- Why Is Blue Light before Bedtime Bad for Sleep?
- How Blue Light Could Damage Cells In Your Eyes?
- Pros and Cons of Blue-Cut/Blue-Control Lenses


































 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.