Hyphema is the collection of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye. The most common cause of hyphema is blunt trauma, though spontaneous hyphemas can occur in the setting of sickle cell disease or other increased bleeding states. Hyphemas are graded based on the degree of blood obscuring the cornea.
Hyphema is the presence of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye, the space between the cornea and the iris. It's typically caused by trauma to the eye, but can also occur after surgery or, rarely, spontaneously.

Symptoms include blurred vision, eye pain, light sensitivity, and visible blood in the eye. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent potential complications like glaucoma or vision loss.
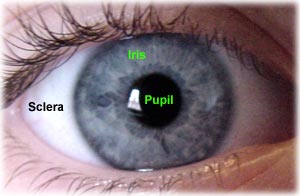
Hyphema is defined as accumulated red blood cells (RBC) in the anterior chamber of the eye. Blood must be grossly visible, either on direct inspection or slit-lamp examination. Blood accumulates from disruption of the vessels of the iris or ciliary body, usually due to trauma or underlying medical conditions. The anterior chamber is the area bounded by the cornea anteriorly, the angle laterally, and the lens and iris posteriorly. This space normally contains clear, aqueous humor, which is produced by the ciliary body and drained through the Canal of Schlemm. The angle, an important anatomic location, is where the trabecular network and the Canal of Schlemm are located. Blockage of this location inhibits aqueous drainage leading to an increase in intraocular pressure.

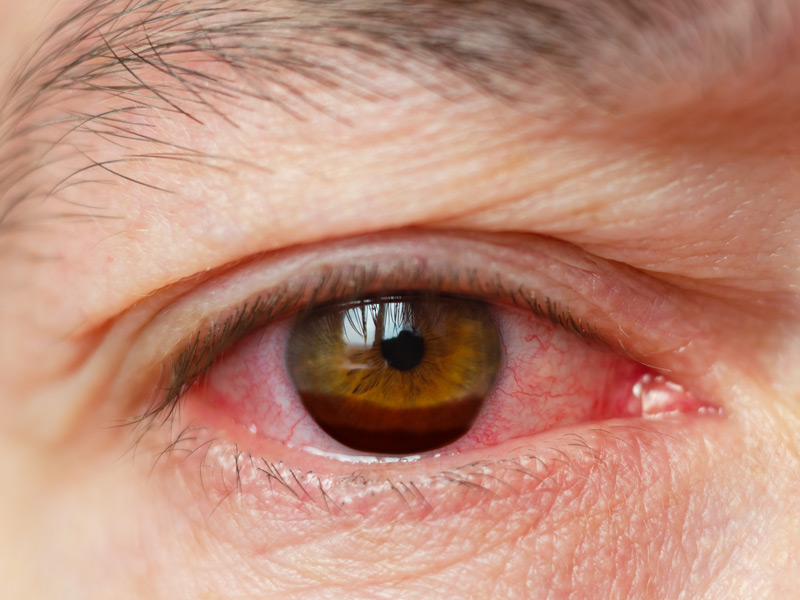

Hyphema Causes and Risk Factors
In rare cases, certain medical problems like juvenile xanthogranuloma and cancer can cause a hyphema.
About 70% of hyphemas happen in children, especially in males ages 10 to 20. They’re usually caused by blunt injuries from activities like:
- Sports
- Industrial accidents
- Falls
- Fights
- Shooting BB and airsoft guns
Less common causes include:
- Eye surgery
- Unusual blood vessels on your iris
- Eye infections from a herpes virus
- Blood clotting problems
- Eye cancers
Some things that affect your blood can make you more likely to have a hyphema, such as:
- Leukemia
- Hemophilia
- Sickle cell disease
- Von Willebrand disease
- Blood-thinning (anticoagulant) drugs
Hyphema Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask whether you’ve ever had an eye injury and what happened before the hyphema. It’s important for them to know if, for example, you were hit in the eye with a baseball or you ran into a tree branch.
The doctor will do an eye exam. This involves:
- A visual acuity test to check how well you can see. They’ll also check the pressure inside your eye (called intraocular pressure).
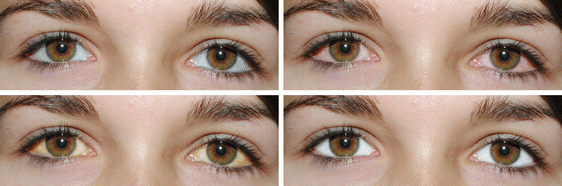
- Looking inside your eye with a special microscope called a slit lamp. A hyphema looks like a clot or layered blood in the front of your eye. If the anterior chamber is filled with blood, it’s called a total, black, or eight-ball hyphema. The doctor can also see if you have a microhyphema, which looks like a haze of red blood cells.
- A CT scan to look at your eye sockets and other parts of your face, if the injury is severe
- Screening for sickle cell disease or thalassemia in people of African descent
What are the symptoms of hyphema?

Let’s focus on the signs and symptoms that indicate hyphema:
Hyphema results in visual disturbance and vision changes- of course the degree of hyphema matters to a great extent in determining visual disturbance. If you have pupillary obstruction, you will be only able to detect some amount of light or identify hand movements.
In hyphema, the aqueous humour is replaced with blood- which eventually leads to bloody eyes. Make sure to book an online appointment in the initial stage- the eye specialists will let you know about the sizable hyphema.
In hyphema, blood in your anterior chamber causes pressure and irritation. It gives rise to unnecessary eye pain after a certain point in time.
Also referred to as photophobia, light sensitivity might end up hurting your eyes and causing headaches. If too much light exposure triggers your eye health, contact a doctor without any further ado.
- Visual Disturbance
- Bloody Eye
- Eye Pain
- Light Sensitivity
Severity and grading of hyphemas
Hyphemas are often graded based on the amount of blood present within the anterior chamber of the eye. This grading system helps healthcare professionals assess the severity of the condition and guide treatment decisions. The most commonly used grading system categorizes hyphemas into four grades: eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- winter 2024
Grade 0 (Microhyphema):
In this grade, there is a small amount of blood that is not easily visible to the naked eye. The blood may be detected using specialized medical equipment.
Grade 1:
In a Grade 1 hyphema, approximately one-third of the anterior chamber is filled with blood. This is when the blood is clearly visible and noticeable to the patient and healthcare provider.
Grade 2:
A Grade 2 hyphema involves blood filling about one-half of the anterior chamber. This level of hyphema is more extensive and can significantly affect vision.
Grade 3:
The most severe grade, Grade 3, occurs when the anterior chamber is filled with blood to the extent that it completely obstructs the view of the iris and pupil. This can lead to a significant decrease in vision and other complications.
The grading of hyphema helps in determining the appropriate course of treatment and monitoring.
Lower-grade hyphemas may be managed with conservative approaches, including rest, elevation, and eye drops to control inflammation and intraocular pressure.
Higher-grade hyphemas, especially Grade 3, are more likely to require closer monitoring and potential medical or surgical intervention to prevent complications such as elevated intraocular pressure or rebleeding.
It’s important to note that the grading system may vary slightly among medical professionals, but the general principles of assessing the amount of blood in the anterior chamber remains consistent.
If you suspect a hyphema, seek immediate medical attention to receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on the severity of your condition.
HOW IS A HYPHEMA TREATED?
When treating a hyphema, the goals are to help clear the blood out, make sure the eye pressure stays normal, and prevent more bleeding. It is important for a person with a hyphema to rest and limit their activity for several days. The head should be kept higher than the feet, even while sleeping, and the eye needs to be protected with a shield. Doctors may prescribe steroid eye drops to help with inflammation and dilating drops (to make the pupil bigger) to help with pain. With a hyphema, it is important not to take aspirin or ibuprofen as they can make the bleeding worse.
Sometimes, the blood from a hyphema can clog normal eye drainage and cause high eye pressure. If the eye pressure stays too high for too long this can cause glaucoma and permanent eye damage. This can be more common in people with sickle cell anemia.

IS SURGERY EVER INDICATED FOR A HYPHEMA?
If the blood does not clear with rest and medication or if the eye pressure is too high for too long, then surgery may be needed to remove the blood.
ARE THERE ANY LONG-TERM EFFECTS FROM A HYPHEMA?
While many people heal well from a hyphema and get their vision back, there can be complications. If the eye bleeds again while healing or other parts of the eye are injured, there may be permanent vision problems. Sometimes the eye’s drainage canals are damaged due to the injury, causing glaucoma (vision loss from high eye pressure). An ophthalmologist can check for damage to the drainage canals with special tools and testing and then decide if ongoing monitoring is needed. It is important for parents, schools, and communities to encourage use of eye protection during sports and play to prevent eye injuries, including hyphema.
More details about hyphema:
Hyphema is essentially blood collecting in the front part of the eye, specifically within the anterior chamber.
Causes:
While trauma is the most common cause, other causes include eye surgery, certain medical conditions (like uveitis or blood disorders), and even spontaneous occurrences.
Symptoms:
Besides visible blood, patients with hyphema may experience pain, blurry or distorted vision, sensitivity to light, and headaches.
Treatment:
Treatment usually involves eye protection (like an eye shield), rest, and pain management. In some cases, more intensive treatments like surgery or hospitalization may be necessary.
Complications:
Untreated hyphema can lead to serious complications such as glaucoma, vision loss, and damage to the eye's structures.
Importance of seeking medical care:
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention from an ophthalmologist if you suspect a hyphema, as prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent long-term vision problems.
Hyphema Treatment
Depending on the severity of a hyphema and associated risk factors, your eye doctor may recommend a combination of the following precautions and treatments:
- Limited physical activity
- Head elevation (including when sleeping)
- Wearing an eye shield
- Frequent follow-up visits for a few weeks or months
- Pain medicine
- Anti-inflammatory medicine (topical or oral)
- Other medications
In the case of a severe hyphema, surgery may be required.
Do not use over-the-counter pain medications that contain aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) if you have a hyphema, as these medications can increase the risk of rebleeding in the eye.
Even if your eye feels fine and you don't notice vision problems, see an eye doctor immediately if you have eye trauma that could cause a hyphema. Make sure to attend all follow-up visits your doctor recommends.
Also, routine eye exams are very important after having a hyphema, as your risk of elevated eye pressure and glaucoma may be higher even years later.
How Can I Prevent A Hyphema?
The best way to avoid a traumatic hyphema is to wear safety glasses or other protective eyewear whenever you are involved in potentially hazardous activities.
Protective sports glasses should be worn when playing baseball, softball, racquetball, basketball, hockey or other sports that pose a risk of trauma to the eyes.
Also, be aware that sports like boxing significantly increase your risk of a traumatic hyphema. And if you participate in paintball games, wear protective headgear that includes a clear, impact-resistant shield that fully protects your face and eyes.
Reference:
- aapos.org/glossary/hyphema
- bceye.com/what-is-a-hyphema
- specscart.co.uk/blog/hyphema
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507802
- webmd.com/eye-health/hyphema-eye-internal-bleeding
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22586-hyphema
- allaboutvision.com/conditions/hyphema







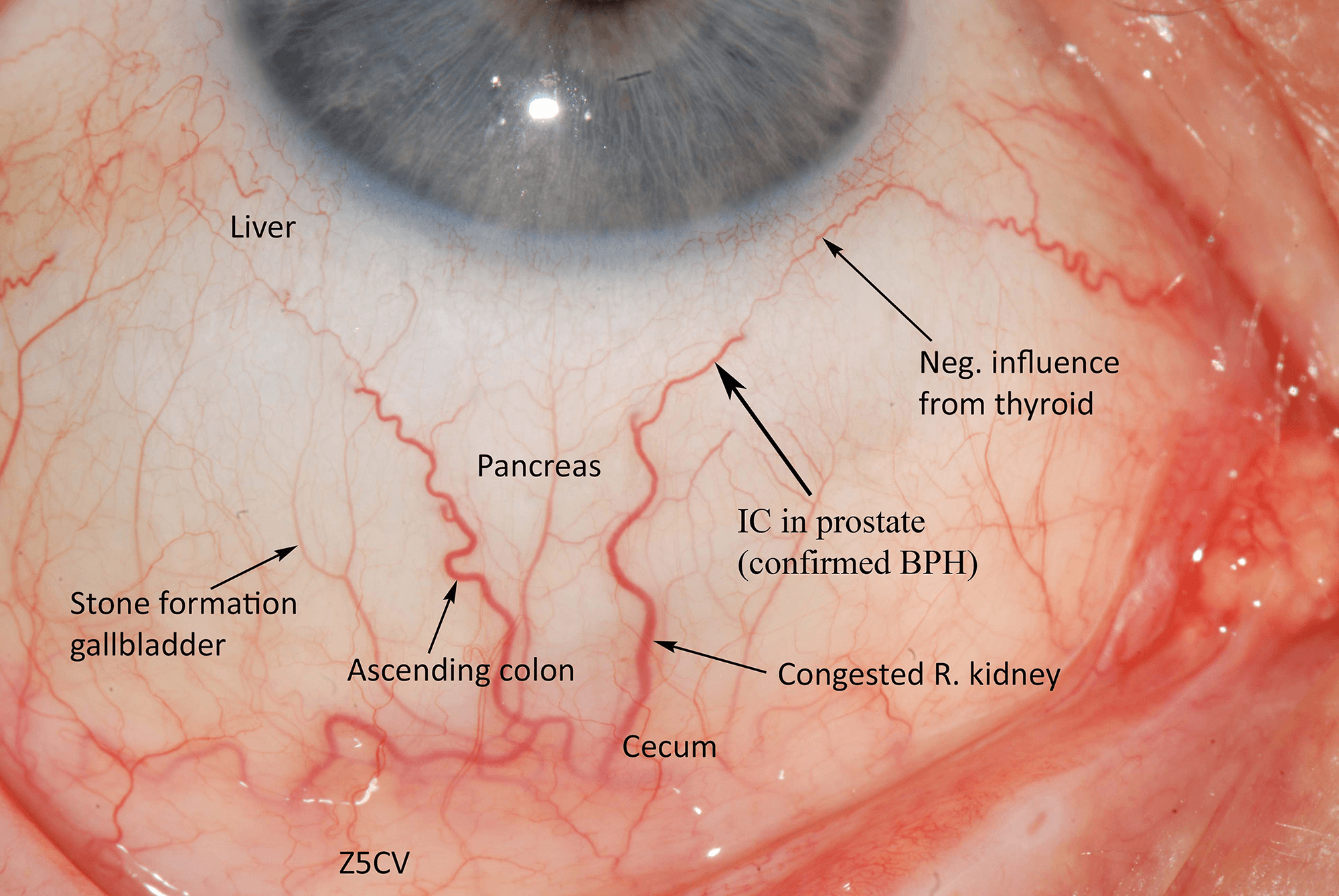


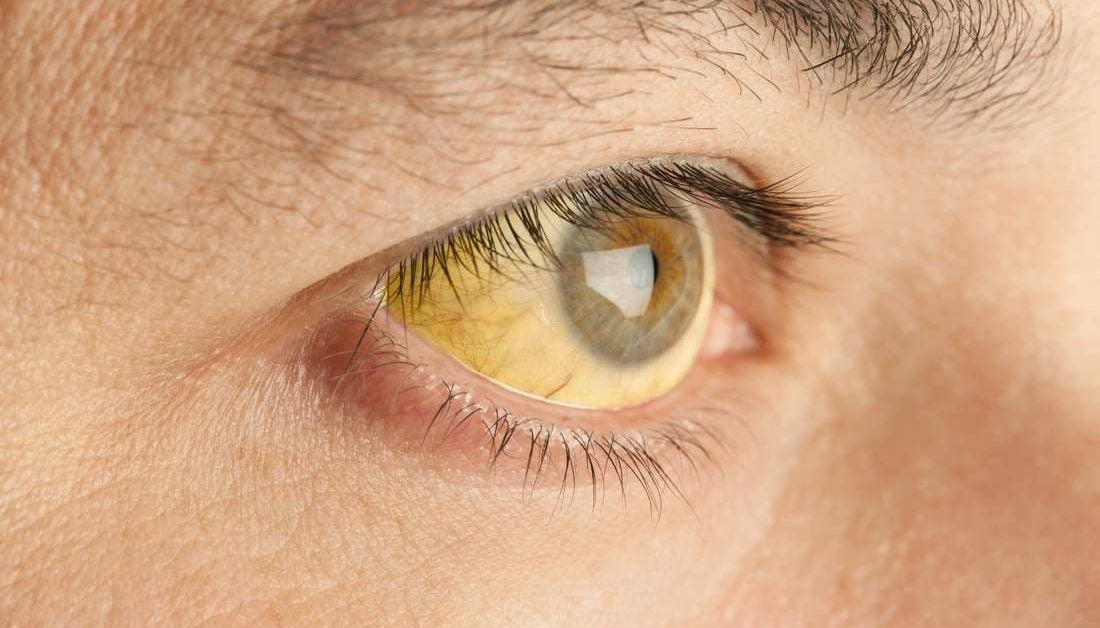
 This right lateral sclera image shows melanin pigment, the brownish coloured 'splotch' you can see in the sclera. This sign is common as a pigmentation spot in a person with darker skin and brown/hazel eyes, representing a genetic predisposition to liver dysfunction. However it does not present the same pathological circumstance as when the melanin sign appears in a blue eyed, fairer skinned person, which is more important/consequential.When the melanin is located close to the iris, it shows mild to moderate liver hardening with associated bacterial infection. When located in an area/s away from the iris, it represents more severe hardening of liver tissue, with sugar system involvement. A substantial diet and lifestyle change, with ongoing liver cleansing and support, is necessary in this circumstance to avoid the condition and sign worsening over time.
This right lateral sclera image shows melanin pigment, the brownish coloured 'splotch' you can see in the sclera. This sign is common as a pigmentation spot in a person with darker skin and brown/hazel eyes, representing a genetic predisposition to liver dysfunction. However it does not present the same pathological circumstance as when the melanin sign appears in a blue eyed, fairer skinned person, which is more important/consequential.When the melanin is located close to the iris, it shows mild to moderate liver hardening with associated bacterial infection. When located in an area/s away from the iris, it represents more severe hardening of liver tissue, with sugar system involvement. A substantial diet and lifestyle change, with ongoing liver cleansing and support, is necessary in this circumstance to avoid the condition and sign worsening over time.





 In many vertebrates, the sclera is reinforced with plates of cartilage or bone, together forming a circular structure called
In many vertebrates, the sclera is reinforced with plates of cartilage or bone, together forming a circular structure called 




 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.