شب کوری برخلاف آنچه از اسمش برمیآید، ازدستدادن کامل بینایی در شب نیست، بلکه در افراد مبتلا به شب کوری توانایی دید در شب یا جاهای کمنور کمتر از حد معمول است. شب کوری برخلاف کوررنگی، بهخودیِ خود اختلال نیست، بلکه نشانهی بیماری دیگری است. شب کوری ممکن است در همهی افراد و در همهی سنین، حتی در کودکان رخ بدهد.

Night blindness (nyctalopia) occurs when a person has significant difficulty seeing in poorly lit environments. While it is relatively normal to experience some blurriness and trouble seeing clearly at night (due to a visual acuity issue), night blindness may be a warning sign of a serious eye condition.
There are two types of light-sensitive cells called rods and cones in the retina. The rods help us see in dim light while the cones enable us to see in brightly-lit settings. Nyctalopia is caused when the rods lose their ability to focus properly at night and under dim light
due to the following:
- Pre-existing health conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetes
- A vitamin A-deficient diet
- Other causes may include medications used to treat glaucoma and a genetic disorder called retinitis pigmentosa.
Retina-related causes of night blindness include: Rare, genetic retinal diseases like cone-rod dystrophy, retinitis pigmentosa (also called rod-cone dystrophy, similar to but not the same as cone-rod dystrophy) or congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB).
بینایی در شب از جهات بسیاری با بینایی در روز متفاوت است. چشم انسان در تاریکی اصولا کوررنگ است، حدت بینایی ضعیف است و چشم تنها بخشی از آنچه را در روز میبیند، در شب هم میتواند ببیند. دلیل آن یک اسکوتوم مرکزی (ناحیهای با کاهش دید) است که در مرکز میدان دید ظاهر میشود و بنابراین چشم نمیتواند آنطور که اشیای متحرک را شناسایی میکند، اشیای ایستا را نیز تشخیص بدهد.
اگر دیدتان در شب ضعیف است، اما طی روز یا در جایی که نور کافی دارد مشکلی ندارید و عادی میبینید، به احتمال زیاد به شب کوری دچارید. در اینصورت نمیتوانید اشیایی را که دیگران در شب بهراحتی میبینند، ببینید و وقتی از محیط روشن به محیطی تاریک میروید، مثلا وارد سالن سینما میشوید، چشمهایتان برای سازگاری و تطابق با اطراف به زمان بیشتری نیاز دارد.

Hemeralopia (from Greek ημέρα, hemera "day"; and αλαός, alaos "blindness") is the inability to see clearly in bright light and is the exact opposite of nyctalopia (night blindness). Hemera was the Greek goddess of day and Nyx was the goddess of night. However, it has been used in an opposite sense by many non-English-speaking doctors. It can be described as insufficient adaptation to bright light. It is also called heliophobia and day blindness.
In hemeralopia, daytime vision gets worse, characterised by photoaversion (dislike/avoidance of light) rather than photophobia (eye discomfort/pain in light) which is typical of inflammations of eye. Nighttime vision largely remains unchanged due to the use of rods as opposed to cones (during the day), which are affected by hemeralopia and in turn degrade the daytime optical response. Hence many patients feel they see better at dusk than in daytime.
Causes
Hemeralopia is known to occur in several ocular conditions. Cone dystrophy and achromatopsia, affecting the cones in the retina, and the anti-epileptic drug Trimethadione are typical causes. Adie's pupil which fails to constrict in response to light; Aniridia, which is absence of the iris; Albinism where the iris is defectively pigmented may also cause this. Central Cataracts, due to the lens clouding, disperses the light before it can reach the retina, is a common cause of hemeralopia and photoaversion in elderly.
C.A.R (Cancer Associated Retinopathy) seen when certain cancers incite the production of deleterious antibodies against retinal components, may cause hemeralopia. Another known cause is a rare genetic condition called Cohen Syndrome (aka Pepper Syndrome). Cohen syndrome is mostly characterized by obesity, mental retardation, and craniofacial dysmorphism due to genetic mutation at locus 8q22-23. Rarely it may have ocular complications such as hemeralopia, pigmentary chorioretinitis, optic atrophy or retinal/iris coloboma, having a serious effect on the person's vision. Yet another cause of hemeralopia is uni- or bilateral postchiasmatic brain injury. This may also cause concomitant night blindness.
Management
People with hemeralopia may benefit from sunglasses. Wherever possible, environmental illumination should be adjusted to comfortable level. Light-filtering lenses appear to help in people reporting photophobia.Otherwise, treatment relies on identifying and treating any underlying disorder.


Nyctalopia /ˌnɪktəlˈoʊpiə/ (from Greek νύκτ-, nykt- "night"; ἀλαός, alaos "blind, not seeing", and ὄψ, ops "eye"), also called night-blindness, is a condition making it difficult or impossible to see in relatively low light. It is a symptom of several eye diseases.
Night blindness may exist from birth, or be caused by injury or malnutrition (for example, a lack of vitamin A). It can be described as insufficient adaptation to darkness. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- summer 2013
The most common cause of nyctalopia is retinitis pigmentosa, a disorder in which the rod cells in the retina gradually lose their ability to respond to the light. Patients suffering from this genetic condition have progressive nyctalopia and eventually their daytime vision may also be affected. In X-linked congenital stationary night blindness, from birth the rods either do not work at all, or work very little, but the condition doesn't get worse. Another cause of night blindness is a deficiency of retinol, or vitamin A, found in fish oils, liver and dairy products.
The opposite problem, the inability to see in bright light, is known as hemeralopia and is much rarer.
What causes night blindness?
Night blindness has many causes, including:
- Myopia
- Glaucoma medications that work by constricting the pupil
- Cataracts
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Vitamin A deficiency
To determine what is causing night blindness, an eye doctor will perform a thorough eye exam and may order any of a number of specialized exams.
How is night blindness treated?
Treatment for night blindness will depend upon its cause. Treatment may be as simple as getting a new eyeglass prescription or switching glaucoma medications, or it may require surgery if the night blindness is caused by cataracts.
If a retinal disease is discovered, the treatment will depend on the type of the disease and will require additional investigation by a retina specialist.





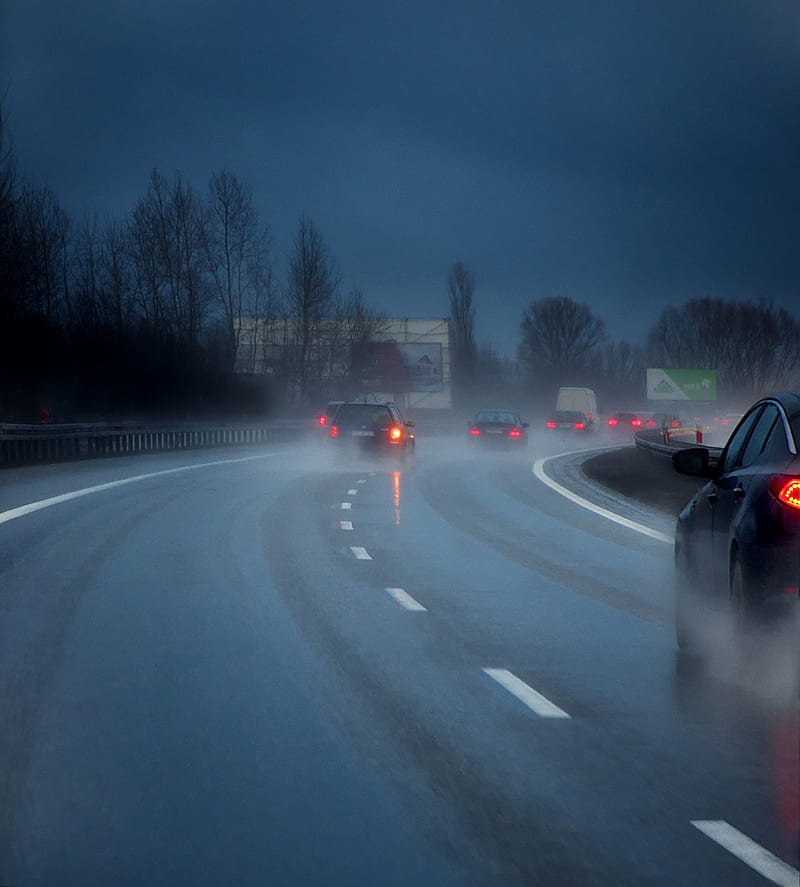
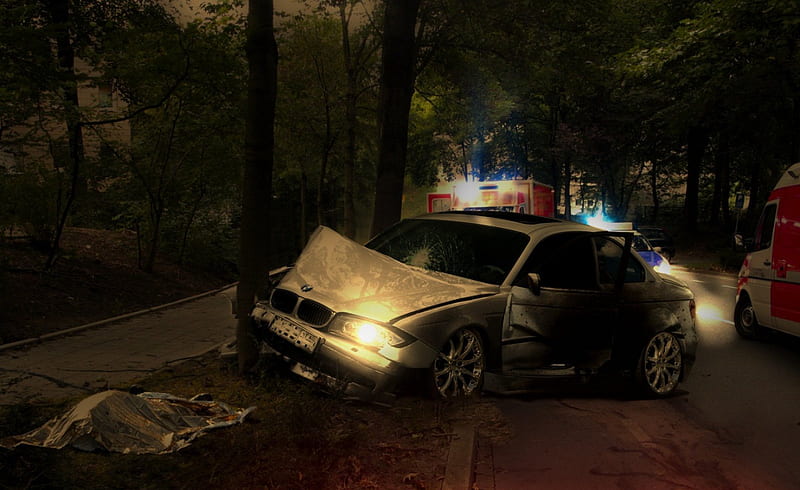
افرادی که به شب کوری دچارند، اغلب نمیتوانند شبها رانندگی کنند. اگر دیدتان در شب ضعیف است، حتما برای معاینه سری به چشمپزشک بزنید.
دلایل شب کوری
شب کوری (nyctalopia) یا ضعف سازگاری با تاریکی، بهعلت اختلال سلولهایی در شبکیهی چشم است که مسئول دید در روشنایی اندک هستند. شب کوری ممکن است نشانهی بیماریهای مختلف اکتسابی یا مادرزادی باشد.
علتهای اکتسابی
آب مروارید (cataracts): افراد مبتلا به آبمروارید اغلب و بهویژه در شب نمیتوانند بهخوبی کتاب بخوانند، رانندگی کنند و حالتهای چهره را تشخیص بدهند.
نزدیکبینی (myopia): گاهی علت شب کوری، نزدیکبینی درماننشده است.
مصرف بعضی داروها: بعضی داروهای آبسیاه یا گلوکوم (glaucoma) مردمک چشم را ضعیف و دید در شب را با مشکل مواجه میکنند.
کمبود ویتامین A: شب کوری یکی از اولین نشانههای کمبود ویتامین A است که معمولا با سوءتغذیه در ارتباط است. کمبود ویتامین اغلب در کودکانی رخ میدهد که دچار سوءتغذیه هستند. این کودکان آنقدر کمسنوسال هستند که نمیتوانند مشکل دیدشان در شب را تشخیص بدهند یا مشکل بینایی خود را بازگو کنند.
علتهای مادرزادی
شب کوری مادرزادی، با یا بدون نزدیکبینی: این مورد به گروهی از اختلالات ناهمگن ژنتیکی (جهش ژنتیکی) برمیگردد. نوعی از شب کوری مادرزادی (choroideremia) فقط روی جنس مذکر اثر میگذارد؛ جنس مؤنث حامل ژنهای مربوطه است، اما نشانههای این بیماری را ندارد؛
رتینیت پیگمنتوزا (Retinitis pigmentosa): این بیماری چشمی درنتیجهی چندین نقص چشمی اتفاق میافتد که منجر به آسیب شبکیه میشوند. افراد مبتلا ممکن است در شب یا روشنایی کم، کاهش دید داشته باشند؛ حتی ممکن است در دید میانی و جانبی نیز مشکل داشته باشند. نشانههای این بیماری در دوران کودکی قابل شناسایی هستند، اما اغلب در بزرگسالی آشکار میشوند.
سندرم آشر (Usher syndrome): این سندرم با کاهش شنوایی و رتینیت پیگمنتوزا شناخته میشود و همانطور که قبلا گفتیم ممکن است باعث شب کوری شود.
آزمایش شب کوری
اگر شبها نمیتوانید بهخوبی ببینید، باید به چشمپزشک مراجعه کنید. در چنین مواردی، چشمپزشک آزمایشهایی انجام میدهد تا مشخص شود آیا به شب کوری مبتلا هستید یا نه، و آیا این شب کوری به بیماری دیگری ارتباط دارد یا خیر.
معاینهی چشم شامل موارد زیر است:
- آزمایشهایی برای بررسی حدت بینایی
- توانایی تشخیص رنگها و واکنش مردمک چشم به روشنایی
- آزمایش انکسار برای بررسی تجویز عینک یا لنز چشم
- معاینهی لامپ اسلیت برای بررسی ساختارهای جلوی چشم ازجمله ملتحمه، قرنیه، پلکها، عنبیه، عدسیها و صلبیه؛
- معاینهی شبکیه برای بررسی وجود هرگونه آسیب در ساختارهای پشت چشم ازجمله زجاجیه، شبکیه و مشیمیه.
ممکن است چشمپزشک الکترورتینوگرافی (Electroretinography) تجویز کند. این آزمایش واکنشهای الکتریکیِ سلولهای استوانهای و مخروطی (سلولهای گیرندهی نور) را در معرض نور بررسی میکند و میتواند عملکرد غیرطبیعی شبکیه، یعنی بخش تشخیص نور چشم را شناسایی کند.
ممکن است آزمایش میدان دید هم روی فرد انجام شود. این آزمایش مشکلات دید میانی و جانبی را که بر اثر گلوکوم و دیگر بیماریهای چشمی یا بهواسطهی مسائلی همچون سکتهی مغزی ایجاد شدهاند، تشخیص میدهد.
درمان شب کوری
اگر شب کوری بر اثر بیماری دیگری بهوجود آمده باشد، معمولا بعد از درمان آن بیماری برطرف میشود. آبمروارید معمولا با جراحی درمان میشود و نزدیکبینی با تجویز عینک یا لنز بهبود مییابد.
در افراد مبتلا به آبسیاه یا گلوکوم، استفاده از داروهای مناسب ممکن است از شدت بیماری بکاهد. افرادی که کمبود ویتامین A دارند، معمولا به مکملهای غذایی و رژیم غذایی سالم واکنش خوبی نشان میدهند. درمان زودهنگام کمبود ویتامین A بسیار مهم است زیرا اگر بدون توجه رها شود، به کوری دائم منجر خواهد شد.
اگر شب کوری ناشی از اختلال مادرزادی باشد، دائمی است و افرادی که از این طریق دچار آسیب شدهاند باید تحت نظر چشمپزشک باشند. این افراد باید بیشتر احتیاط کنند تا از آسیبهایی که ممکن است بر اثر دید ضعیف در شب بهوجود بیایند، در امان بمانند.
برای درمان شب کوری، باید بهطور منظم تحت نظر چشمپزشک باشید. شاید برای رانندگی در شب به عینک نیاز داشته باشید. برای کاهش خطر آسیب به خود و دیگران هنگام فعالیتهای شبانه همچون رانندگی، تشخیص زودهنگام این بیماری بسیار اهمیت دارد.
Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is a nutrient that plays an essential role in the function of your retina. The retina is located in the back of your eye and is responsible for image processing. Without enough vitamin A in your body, your retina can’t work as well as it should. A Vitamin A deficiency is often the cause of diet or underlying health conditions. Luckily, plenty of foods are rich in vitamin A, such as kale, seaweed, carrots, fish oils, dairy, and much more.
Although incorporating vitamin A-rich foods into your diet is a great way to promote the longevity of your eye health, you should always tell your eye doctor if you’re experiencing any changes in your vision.
Zinc Deficiency
Zinc is an essential nutrient for eye health and retina function as well. This important mineral can even help prevent eye diseases like macular degeneration. However, when your body doesn’t get enough zinc, this can cause vision problems such as night blindness.
A great way to increase your zinc intake naturally is through your diet. Meats, shellfish, dairy, eggs, and legumes are all excellent sources of zinc.
پیشگیری از آسیب ناشی از شب کوری
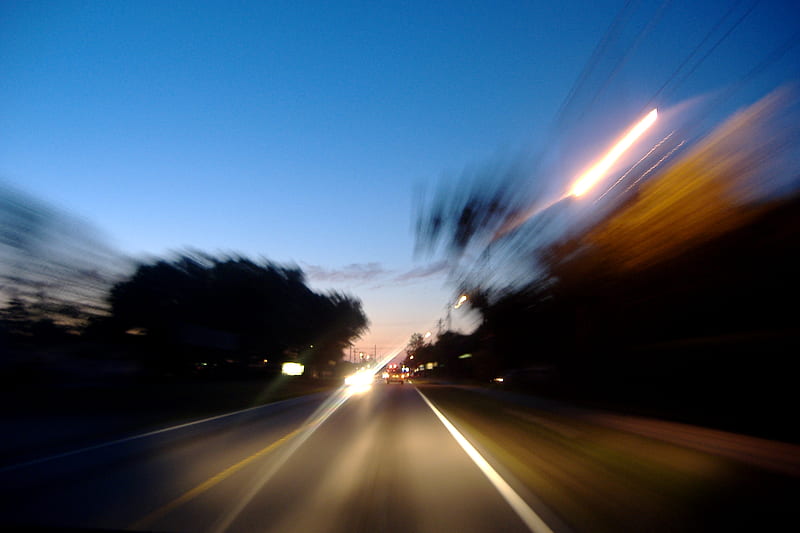
رانندگی در شب برای این بیماران خطرناک است، زیرا سرعت واکنش راننده هنگام رانندگی به دید او بستگی دارد. حتی دید طبیعی در شب بسیار محدودتر از روز است. رانندگان مسن در مقایسه با جوانترها، هنگام رانندگی در شب دید کمتری دارند. برای مثال رانندهی پنجاه ساله، به نوری دوبرابرِ رانندهی سی ساله نیاز دارد.
بهترین راهِ محافظت از خودتان در برابر آسیبهای ناشی از شب کوری، اجتناب از رانندگی در شب است. سعی کنید صرفا در طول روز رانندگی کنید. کسانی که به شب کوری دچارند ممکن است حتی زیر نورهای مصنوعی هم با مشکل مواجه شوند. اگر واجب است شبها رانندگی کنید، نکاتی را برای ایمنی بیشتر رعایت کنید. مثلا با تمیز کردنِ شیشهها و چراغهای جلوی خودرو، دید خود را افزایش بدهید؛ با سرعت کمتری رانندگی کنید تا در صورت بروز اتفاقات غیرمنتظره، بتوانید سریعتر واکنش نشان بدهید.
Reference:
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10118-night-blindness-nyctalopia
- millervision2020.com/trouble-seeing-at-night-all-about-night-blindness
- heinfolist.com/php/SummaryGet.php?FindGo=hemeralopia
- neovisioneyecenters.com
- researchgate.net/figure
- clevelandclinic.org
- chetor.com/119356
- en.wikipedia.org
- retinasocal.com






















 When fishing, wearing polarized sunglasses will allow people to see into the water more clearly and accurately. When the sun is out, it can reflect off the water and cause the visibility to go down. When fishing, many people need to see into the water. Polarized sunglasses take a lot of the glare off the water allowing people to see what is below. This is helpful when boating also. In order to protect the boat from jagged rocks just below the surface, people can navigate the boat around these objects because they saw them ahead of time. These sunglasses can cave people from a wide variety of accidents both in the water and on the road.
When fishing, wearing polarized sunglasses will allow people to see into the water more clearly and accurately. When the sun is out, it can reflect off the water and cause the visibility to go down. When fishing, many people need to see into the water. Polarized sunglasses take a lot of the glare off the water allowing people to see what is below. This is helpful when boating also. In order to protect the boat from jagged rocks just below the surface, people can navigate the boat around these objects because they saw them ahead of time. These sunglasses can cave people from a wide variety of accidents both in the water and on the road.




 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.