What is retinoschisis?
Retinoschisis is a condition that happens when your retina divides into two or more layers. Schisis means a split or a cleft. Retinoschisis affects the light-sensing layer of your retina and the layer of cells that transmits signals to your brain through the optic nerve.
This division of the layers can affect how well you see. Splits can occur in the center of the retina but are more likely at the periphery (outer edges).
What are the signs and symptoms of retinoschisis?
You may have no symptoms of the disease. If you do, symptoms that may happen with juvenile X-linked retinoschisis include:
- Eyes that turn toward your nose (crossed eyes).
- Eyes that move uncontrollably from one side to the other (nystagmus).
- Loss of central (foveal) vision or side (peripheral) depending on where the split occurs.
- Having farsightedness.
If you’ve developed acquired retinoschisis, you might find that you can’t see clearly on either side (loss of peripheral vision). You may not have any symptoms at all.
If you have retinoschisis and it becomes severe, or you also have retinal detachment, you may notice:
- Floaters and flashers.
- Distorted images.
- Loss of central (foveal) vision or side (peripheral) depending on where the split occurs.
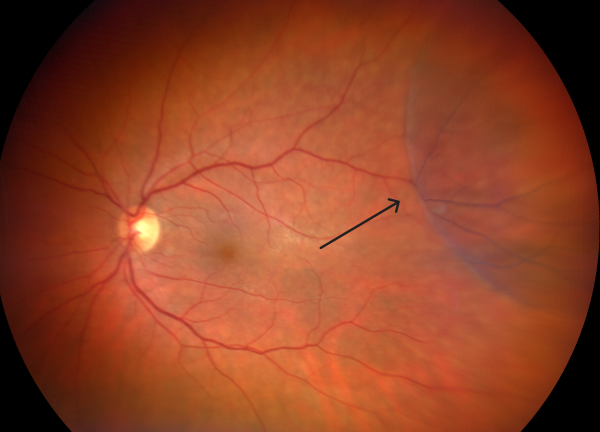
Are X-linked disorders male or female?
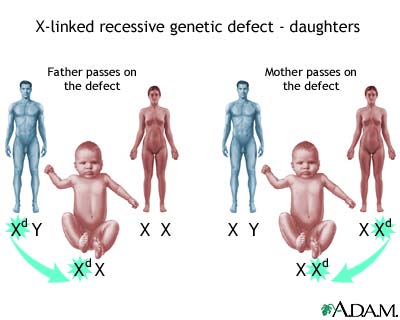
X-linked recessive diseases most often occur in males. Males have only one X chromosome. A single recessive gene on that X chromosome will cause the disease. The Y chromosome is the other half of the XY gene pair in the male.

Patterns of inheritance
Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance in a royal family
In humans, inheritance of X-linked recessive traits follows a unique pattern made up of three points.
- The first is that affected fathers cannot pass X-linked recessive traits to their sons because fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons. This means that males affected by an X-linked recessive disorder inherited the responsible X chromosome from their mothers.
- Second, X-linked recessive traits are more commonly expressed in males than females.This is due to the fact that males possess only a single X chromosome, and therefore require only one mutated X in order to be affected. Women possess two X chromosomes, and thus must receive two of the mutated recessive X chromosomes (one from each parent). A popular example showing this pattern of inheritance is that of the descendants of Queen Victoria and the blood disease hemophilia.
- The last pattern seen is that X-linked recessive traits tend to skip generations, meaning that an affected grandfather will not have an affected son, but could have an affected grandson through his daughter. Explained further, all daughters of an affected man will obtain his mutated X, and will then be either carriers or affected themselves depending on the mother. The resulting sons will either have a 50% chance of being affected (mother is carrier), or 100% chance (mother is affected). It is because of these percentages that we see males more commonly affected than females.
X-Linked Retinoschisis (XLRS)
A rare disorder involving multiple structure of the eye characterized by reduced visual acuity in males due to juvenile macular degeneration. Clinical features such as vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, and neovascular glaucoma can be observed in advanced stages.
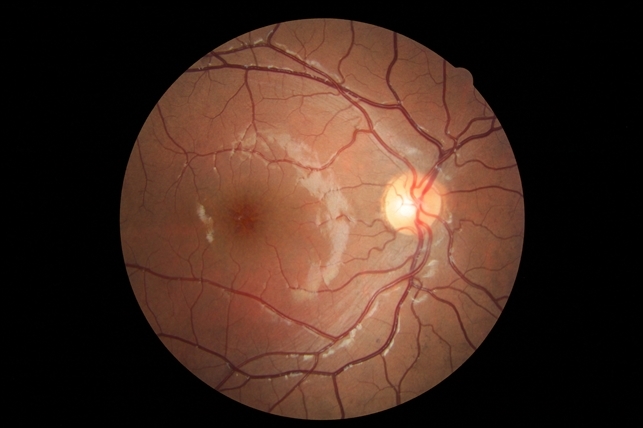
X-linked Retinoschisis or X-Linked Juvenile Retinoschisis is a rare congenital disease of the retina caused by mutations in the RS1 gene, which encodes retinoschisis, a protein involved in intercellular adhesion and likely retinal cellular organization.
X-linked retinoschisis, with a prevalence of about 1 in 15,000 to 30,000, is one of the main causes of juvenile macular degeneration in males. It is characterized by symmetric bilateral macular involvement beginning in the first decade of life.
It is caused by a large variety of mutations in the RS1 gene on Xp22.1-p22.3, which encodes the protein retinoschisis. This protein is involved in intercellular adhesion and likely retinal cellular organization. X-linked retinoschisis is inherited in an X-linked manner with complete penetrance and variable expressivity.
Most affected individuals are males, as heterozygous females are rarely affected. However, retinoschisis has been reported in non-consanguinous females. The phenotype can be markedly variable even within the same genotype and can involve the peripheral retina.
Reference:
- educate.choroida.com/2023/02/03/x-linked-retinoschisis-genetics-and-management
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24310-retinoschisis
- fightingblindness.org/diseases/x-linked-retinoschisis-xlrs
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-linked_recessive_inheritance
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002051.htm
 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.