Astigmatism (uh-STIG-muh-tiz-um) is a refractive error that prevents sufferers from seeing objects clearly from a distance or up close. Astigmatism may occur in varying degrees in each eye and can accompany myopia or hyperopia. Mild astigmatism is usually not noticeable, or causes only slight blurriness, while severe astigmatism causes objects to appear blurry at any distance. Approximately 80 percent of Americans have some degree of astigmatism, but many cases do not require correction.
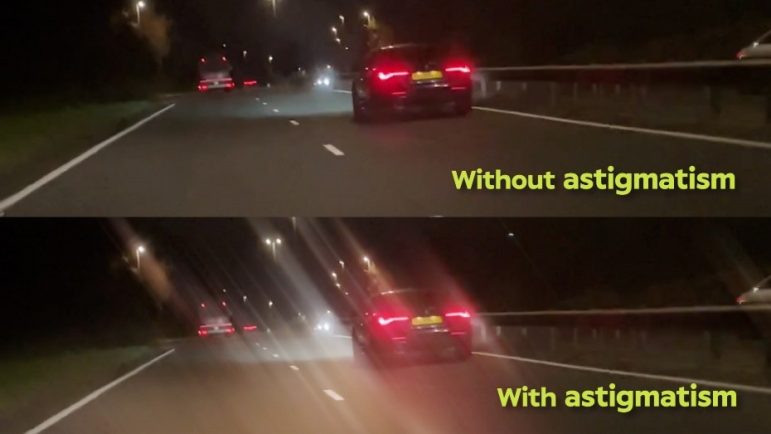

In low-light conditions, blurry vision associated with astigmatism can become worse because when the lighting dims, your pupil dilates to let in more light.The more light that is let in, the more light that is scattered. This scattered light causes unfocused vision, as well as halos around bright lights and even night blindness.Bright headlights from oncoming and rear traffic can become particularly distorted, creating ‘lines’ of light around the headlight.
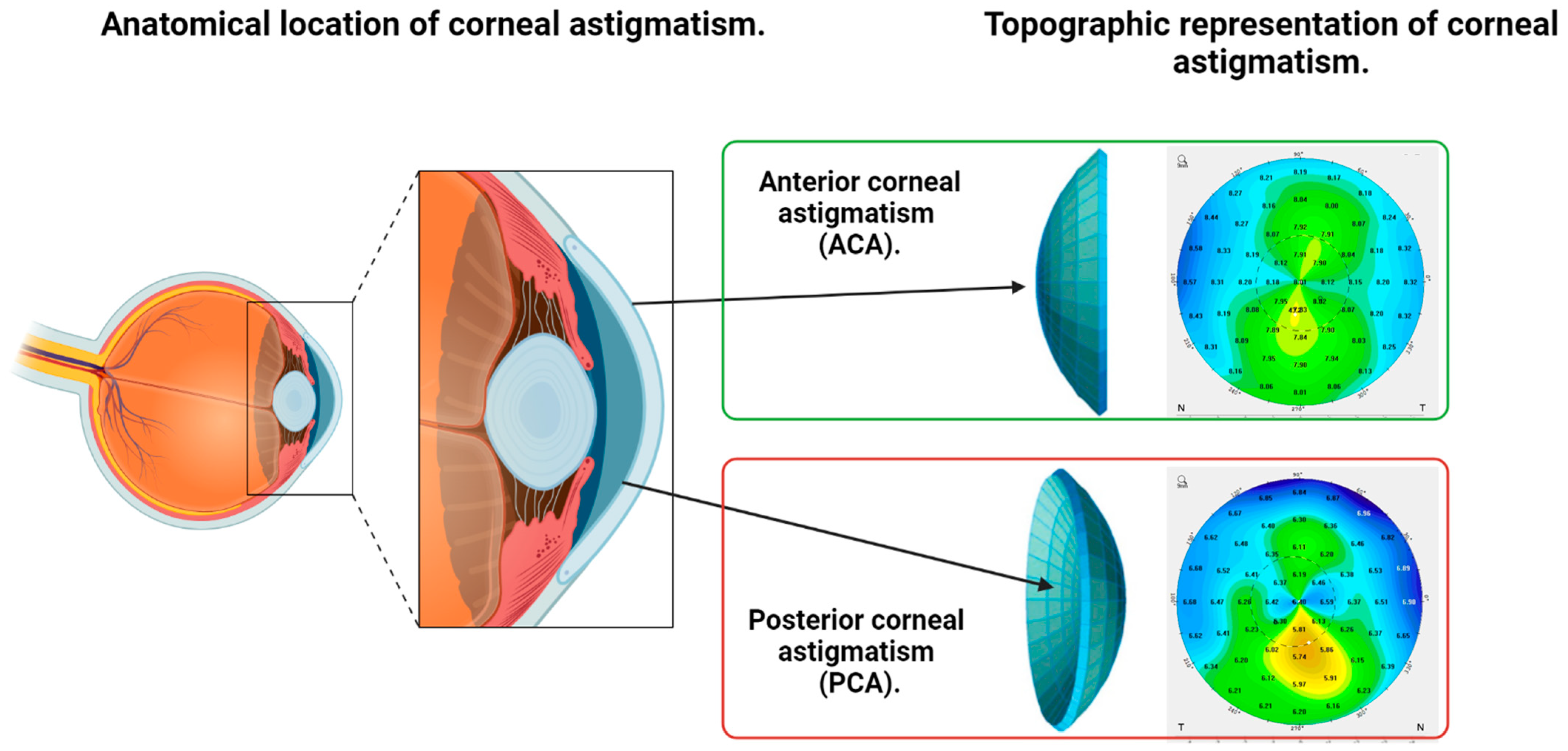
A normal cornea is shaped like a perfect sphere. The eye’s natural lens is also curved in equal degree in all directions. The corneas or lenses of people with astigmatism do not have equal curves. One side may be steeper than the other, making the cornea look more like a football than a basketball. Because of this, light entering the eye is not focused correctly on the retina, resulting in a blurred image.[1]
What are the signs and symptoms of astigmatism?
Signs and symptoms include:
- Eyestrain
- Squinting
- Headaches
- Difficulty driving at night
- Distorted or blurred vision at all distances [5]
If you experience any of these symptoms, visit your eye care professional. If you wear glasses or contact lenses and still have these issues, a new prescription might be needed.
When to see a doctor

If your quality of vision detracts from your enjoyment of activities or interferes with your ability to perform everyday tasks, see an eye doctor. An eye doctor can determine whether you have astigmatism, and if so, to what degree. He or she can then advise you of your options to correct your vision.
If you're a healthy adult older than 40, have your eyes examined about every two to four years until age 55. After age 55, have them checked every one to three years for signs of eye disease or problems, and then every one to two years after age 65. If you have eye problems, such as astigmatism, you may need to have your eyes checked more frequently. If you're at risk of certain eye diseases, such as glaucoma, or you have diabetes, check with your doctor to see how often you need to have your eyes examined.
Astigmatism occurs when your eyes are unable to focus light rays onto a single point, which is the ideal process. Usually this disorder causes blurry vision, possible sensitivity to light, eye discomfort and potentially headaches.
In astigmatism, the cornea has multiple powers, leading to multiple points of focus and blurry vision. People with astigmatism may also report double vision or ghost images.
What are the types of astigmatism?
There are three types of of astigmatism: [11]
Lenticular astigmatism.
Affects the lens instead of the cornea. The lens allows the images to reach the retina, and this type of astigmatism makes it have variations.
Myopic astigmatism.
This type of astigmatism happens when astigmatism and nearsightedness are combined, causing the two curves to focus in front of the retina.
Hyperopic astigmatism.
This happens when farsightedness is combined with astigmatism, causing the two curves to focus behind the retina.
Mixed astigmatism.
When one eye is farsighted, while the other is nearsighted
Astigmatism can also be classified as regular or irregular:
- Regular astigmatism means that the two curves are 90 degrees apart, while irregular astigmatism is not 90 degrees apart from each other.
- Irregular astigmatism can be caused by an eye injury, eye trauma, surgery or an eye condition called keratoconus, which makes the cornea gradually thinner.
Tests and diagnosis
To diagnose astigmatism, your eye doctor may:
Measure reflected light. By measuring light reflected from the surface of your cornea, a device known as a keratometer quantifies the amount and orientation of corneal astigmatism.
Measure the curvature of your cornea. Using light to project rings on to your cornea, a device called a keratoscope measures the amount of curvature to your cornea's surface and can confirm the presence of astigmatism. Observation through the keratoscope of the reflection of light from your cornea and inspection of the shape and spacing of the rings provide information about the degree of astigmatism.
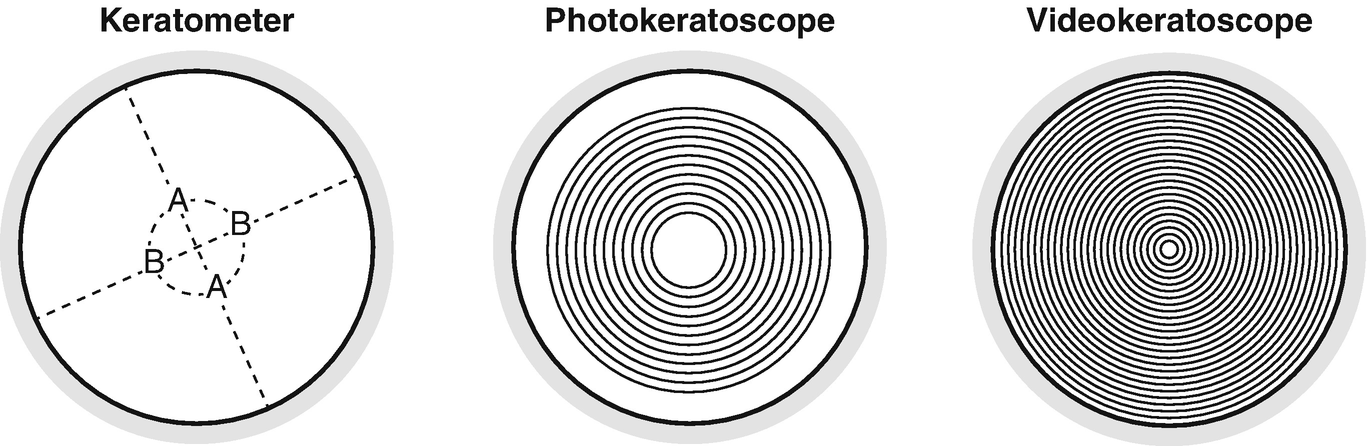
To measure the change in corneal surface curvature, a process called corneal topography is used. Corneal topography uses a videokeratoscope, which is a keratoscope fitted with a video camera.[2]
Levels of Astigmatism
Astigmatism is measured in units of diopters. In a prescription, plus and minus signs in the ‘cylinder’ box indicate the astigmatism prescription, which is then followed by numbers indicating the location (axis) of astigmatism. Here is a rough breakdown of the different degrees of astigmatism:
- 0.25 to 0.75 diopters = mild astigmatism
- 1.00 to 2.50 diopters = moderate astigmatism
- 2.75 to 4.75 diopters = severe astigmatism
- 5.00 diopters or higher = extreme astigmatism
To prescribe corrective wear for astigmatism, measurements are taken from a vertical and horizontal, or oblique approach, forming an axis. This is done because light enters the eye from different directions. Both the vertical and horizontal measurements will be different with astigmatism.
In general, higher levels of astigmatism show a greater disparity between two prescriptions, and with milder astigmatism, the values are much closer to each other.

The following are a few other abbreviations you may encounter on your eyeglass prescription:
SVD - Single Vision Distance, or glasses for distance only
SVN - Single Vision Near, or glasses for reading only
Sphere - Spherical power has the same power in all meridians
Cylinder - A cylinder power corrects astigmatism and represents the difference in the greatest power of the eye and weakest power of the eye, usually separated by 90 degrees.
Axis - indicates the angle (in degrees) between the two meridians of an astigmatic eye
PD - (pupillary distance, or distance between the centers of the two pupils between the eyes) This measurement is essential to designing glasses that comfortable to wear and optically perfect.
Prism - Prism is not commonly prescribed. It is often prescribed to displace the image in a certain direction for patients with crossed-eye (strabismus) or other eye muscle or focusing disorders.[3]
Diagnosis

Patients seek treatment because of blurred vision. A variety of tests can be used to detect astigmatism during the eye exam. The patient may be asked to describe the astigmatic dial, a series of lines that radiate outward from a center. People with astigmatism will see some of the lines more clearly than others.
Cover one eye with your hand, without pressing on the lid, and take the test.
Cover the other eye and begin the test again. If some of the lines appear grayer and some blacker, you probably have an astigmatism - consult your eye care specialist.
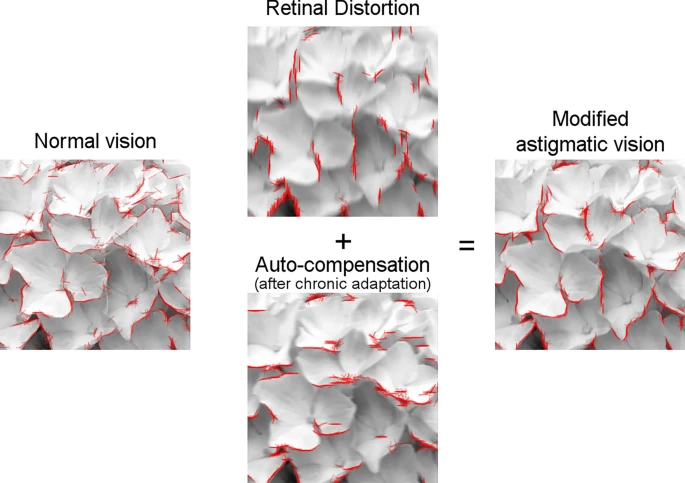
Simulation of the compensatory effect on chronic astigmatism when an image of a hydrangea is presented. The effect of the astigmatic blur and the automatic compensation were simulated for visualization purposes, according to the mechanisms of the adaptation model described in the Results and Methods sections. The edges of each image were detected with the Sobel operator (red). The edges are intact in the image of normal vision but severely biased vertically in the astigmatic retinal image. After being counterbalanced by the inversely biased edges of the automatic compensation, the vision with chronic astigmatism partly restores the original edges.
One diagnostic instrument used is the keratometer. This measures the curvature of the central cornea. It measures the amount and direction of the curvature. A corneal topographer can measure a larger area of the cornea. It can measure the central area and mid-periphery of the cornea. A keratoscope projects a series of concentric light rings onto the cornea. Misshapen areas of the cornea are revealed by noting areas of the light pattern that do not appear concentric on the cornea. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- summer 2013
Because these instruments are measuring the cornea, it is also important to have a refraction in case the lens is also contributing to the astigmatism. The refraction measures the optics or visual status of the eye and the result is the eyeglass prescription. The refraction is when the patient is looking at an eye chart and the doctor is putting different lenses in front of the patient's eyes and asks which one looks better.

Proposed videokeratography pattern classification scheme. PSBT=prolate symmetric bow tie, PABT=prolate asymmetric bow tie, OSBT=oblate symmetric bow tie, OABT=oblate asymmetric bow tie, PI=prolate irregular, OI =oblate irregular, SF=steep/flat, LS=localised steep. Most of the patterns can be seen as a continuum, with some of them changing into different patterns (arrows) after manipulation of post-PKP astigmatism, by removal or adjustment of sutures. Blue and red colours imply flat and steep areas respectively, as in the conventional topographic map representation.[6]




Keratoconus (ker-uh-toe-KOH-nus) is a naturally occurring weakening of the cornea, characterized by its progressive asymmetric thinning and steepening. Keratoconus typically begins in the teens or 20s, progresses over a decade, and results in significant visual dysfunction, reduced quality of life, and permanent changes in the patient’s lifestyle.[7]
Keratoconus is an eye condition in which your cornea — the clear, dome-shaped front of your eye — gets thinner and gradually bulges outward into a cone shape.
Causes of Astigmatism [14]

Astigmatism is primarily caused by irregularities in the shape of the cornea or lens of the eye. The specific causes can include:
- Corneal Shape: Irregularities in the curvature of the cornea, such as a football-shaped cornea instead of a spherical one, can lead to astigmatism.
- Lens Abnormalities: Changes in the shape of the eye's crystalline lens can also contribute to astigmatism.
- Genetics: Astigmatism frequently has a hereditary component, which means that it can occur in families.
- Eye Injuries or Surgeries: Trauma to the eye or certain eye surgeries can result in irregular astigmatism.
- Keratoconus: A condition where the cornea progressively thins and bulges outward, leading to astigmatism.
- Changes with Age: Astigmatism can develop or change as a person ages.
- Eye Conditions: Certain eye conditions, such as corneal scars or degenerations, can cause irregular astigmatism.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged and intense use of the eyes for tasks like reading or computer work may contribute to eyestrain but is not a direct cause of astigmatism.
OCULUS PENTACAM. Refractive display of a patient with mild keratoconus. The upper left map (anterior curvature) shows nonorthogonal principal meridians, which is a hallmark of irregular astigmatism. The upper right (anterior elevation) and lower right (posterior elevation) show the classic positive island of elevation. The corneal thickness map (lower left) shows a moderately thinned cornea.
Treatment

Astigmatism can be treated by the use of cylindrical lenses. They can be in eyeglasses or contact lenses. The unit of measure describing the power of the lens system or lens is called the diopter (D). The lenses are shaped to counteract the shape of the sections of cornea that are causing the difficulty.
Because the correction is in one direction, it is written in terms of the axis the correction is in. On a prescription, for example, it may say −1.00 × 180°. Cylinders correct astigmatism, minus spheres correct myopia, and plus spheres correct hyperopia.
There is some debate as to whether people with very small amounts of astigmatism should be treated. Generally, if visual acuity is good and the patient experiences no overt symptoms, treatment is not necessary. When treating larger amounts of astigmatism, or astigmatism for the first time, the doctor may not totally correct the astigmatism. The cylindrical correction in the eyeglasses may make the floor appear to tilt, thus making it difficult for the patient at first.
Generally, the doctor will place lenses in a trial frame to allow the patient to try the prescription at the exam. It may take a week or so to get used to the glasses, however, if the patient is having a problem they should contact their doctor, who might want to recheck the prescription.[4]
Reference:
- eyehealthweb.com
- mayoclinic.com/diseases-conditions/keratoconus/symptoms-causes/syc-20351352
- vision.about.com
- encyclopedia.com
- nei.nih.gov
- bjo.bmj.com/content/83/4/403 The British Journal of Ophthalmology (BJO)
- optometrytimes.com/view/when-do-you-diagnose-keratoconus
- nature.com/articles/s41598-022-07788-y
- droitwichstandard.co.uk/news/droitwich-specsavers-raising-awareness-of-common-eye-condition-affecting-drivers
- aao.org/eyenet/article/handling-irregular-astigmatism - American Academy of Ophthalmology
- kideyedoc.com/pediatric-eye-associates-talks-astigmatism-kids-ophthalmologist
- cinemaeyehonors.com/retrospective
- davidshanahan.com.au/eye-care/astigmatism-treatment
- jrsh.co.in/astigmatism

 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.