Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness, longsightedness or hypermetropia, is a defect of vision caused by an imperfection in the eye (often when the eyeball is too short or the lens cannot become round enough), causing difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases causing a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance. As an object moves toward the eye, the eye must increase its optical power to keep the image in focus on the retina. If the power of the cornea and lens is insufficient, as in hyperopia, the image will appear blurred.[1]
What does it mean to show farsightedness?
People with hyperopia can experience
- blurred vision,
- asthenopia,
- accommodative dysfunction,
- binocular dysfunction,
- amblyopia, and strabismus.
Classification of hyperopia
- Simple hyperopia
- Pathological hyperopia
- Functional hyperopia
- Ornithological hyperopia
Causes
Hyperopia can be caused by sinus infections, injuries, migraines, aging or genetics.
How is farsighted vision corrected? eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- summer 2011
Farsightedness
Farsighted (also called hyperopia) is a term to describe an eye condition that lets you clearly see objects “far” or distant in your field of vision, while objects that are near appear blurry or hazy. Due to the nature of this type of vision problem, farsightedness can affect vision in different ways.
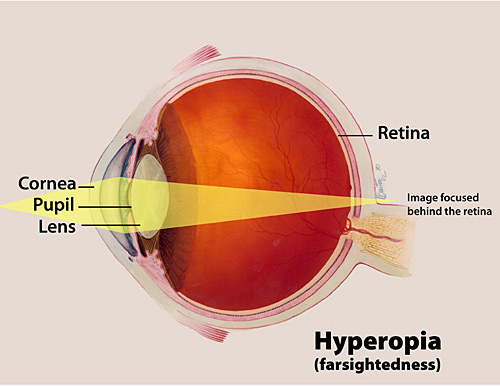
Farsightedness happens in eyes that are incorrectly focusing images behind the retina rather than directly on it. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the human eye responsible for processing images.

Farsighted vision is treated with corrective lenses like eyeglasses or contact lenses, and can also be treated surgically with types of surgery. Farsighted vision can develop in children or adults, and between 5 and 10 percent of all Americans are considered to be farsighted.
Persons who are extremely nearsighted, have diabetes, or have had cataract surgery are also more likely to report eye floaters.
Farsightedness Symptoms
Symptoms of farsightedness include eyes that feel tired or strained, headaches, squinting and blurred vision, especially when viewing objects that are near. But symptoms can vary person to person based on the degree of farsighted vision; some may notice little visual impairment, while others may have blurred or hazy vision for objects at distance and nearby.
Farsighted vision can develop at any time, and happens in both children and adults.
Farsightedness develops when the eyeball becomes “shorter” than it should be, moving the “focal point” of the images we see from on top of the retina, to behind the retina. Abnormalities in the eye’s lens or cornea can also cause farsighted vision.
Reference:
1.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperopia 2.bausch.co.uk 3.eyeglassguide.com
 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.