Leukocoria is when your eye's pupil reflects white, silvery, gray or yellowish instead of red. The color difference is because light is reflecting off something other than the red-reflecting retinal tissue at the back of your eye. It can be a sign of serious or dangerous eye conditions.[1]
A white reflex (leukocoria) is due to a white media opacity such as a cataract involving the anterior aspect of the lens , retinoblastoma, toxocara, Coats disease or a retinal defect called a chorio-retinal coloboma.[6]
Leukocoria:
Other names Leucocoria, white pupillary reflex
Leukocoria (also white pupillary reflex) is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine, but leukocoria can also occur in animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum.[2]
Leukocoria is a medical sign for a number of conditions, including Coats disease, congenital cataract, corneal scarring, melanoma of the ciliary body, Norrie disease, ocular toxocariasis, persistence of the tunica vasculosa lentis (PFV/PHPV), retinoblastoma, and retrolental fibroplasia.
Because of the potentially life-threatening nature of retinoblastoma, a cancer, that condition is usually considered in the evaluation of leukocoria. In some rare cases (1%) the leukocoria is caused by Coats' disease (leaking retinal vessels).
When someone shines a light at your eyes, it should cause a faint red reflection in your pupil. That’s called the “red reflex,” and it happens because of light bouncing off the retina at the back of your eye. A common way to see this is by taking a flash-illuminated picture of someone looking directly at you.
If something else is in the way and reflects the light instead of the retina, that can cause leukocoria. This symptom mainly affects children, but it can also happen in adults. But the conditions that usually cause it in adults aren’t as likely to be dangerous.
What is a red reflex versus a white reflex? [3]
The retina is a layer of tissue at the back of the eye. It is responsible for taking the light and images that come through the eye’s lens and sending them to the brain. The blood vessels inside as well as right behind the retina cause it to appear orange or red.
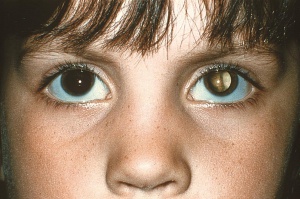
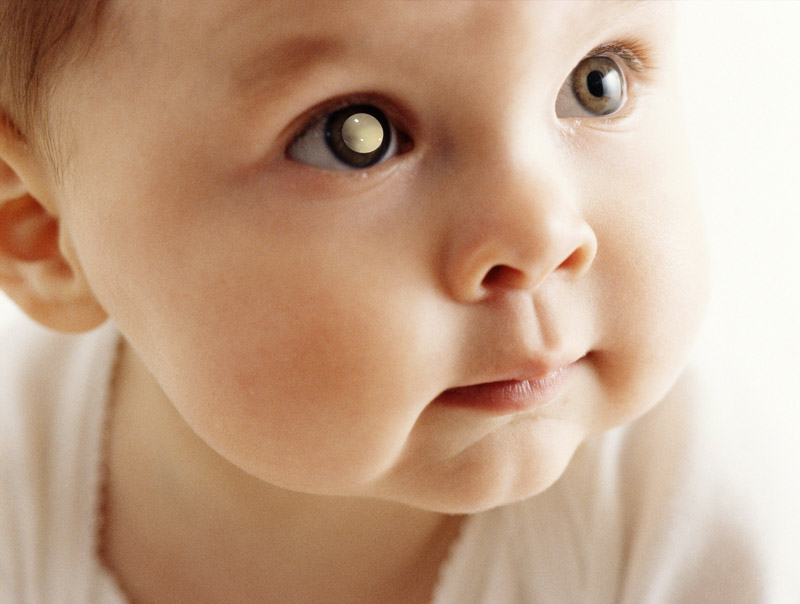
When light shines on a healthy pupil, it often reflects red. This is because the light that isn’t absorbed by the retina bounces back with the color of the retina itself. This is known as the “red reflex.” A common example of this reflex is the occurrence of red eyes in a photograph.
When something blocks the retina or causes an abnormal reflection, the light is either absent or reflects white. This “white reflex” can also be noticeable in photographs. However, the use of red eye removal software may make it difficult to recognize. It is important to seek an evaluation from an eye doctor if a white reflex is present.
What Causes Leukocoria? [7]
Cataracts. Cataracts occur when you have a cloudy area in the lens of your eye. They're very common as you age and can be easily corrected by surgery.
Retinal detachment. A retinal detachment occurs when the retina, a thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye, pulls loose from its normal position. There are usually other symptoms accompanying retinal detachment, such as blurred vision, flashes of light, or a shadow over your field of vision. A retinal detachment is an emergency that should be treated immediately.
Endophthalmitis. Endophthalmitis is an infection of the tissues or fluid inside of your eyeball. It can be caused by bacteria or fungi getting inside of your eyeball following an injury or surgery. It can also spread from an infection in another part of your body. Endophthalmitis is an urgent medical emergency that can cause blindness if not treated right away.
Coats' Disease. Coats' disease is an abnormality affecting the blood vessels inside of your eye. These blood vessels provide blood and oxygen to your retina. Coats' disease causes these blood vessels to become large, twisted, and leaky. The normal flow of blood is prevented, and fluid leaks out of the blood vessels, causing fatty material to build up in the retina. If too much fluid builds up, it can cause your retina to detach.
Retinoblastoma. Retinoblastoma is a rare form of eye cancer that primarily affects children. Leukocoria is one of the primary symptoms of retinoblastoma. Other symptoms can include poor vision, eye redness or swelling, or eyes that appear to be looking in different directions.
Retinoblastoma can occur in one or both eyes and spread to other areas of the body such as the brain or spine. There is no known cause of retinoblastoma, although in some cases, a tendency may be inherited. eResearch by Navid Ajamin -- winter 2025
Power difference. Sometimes, an abnormal red reflex results from a power difference between your eyes. These cases aren't usually serious and are easily treated.
Many different conditions can cause leukocoria, ranging from minor to life-threatening, so it should always be evaluated quickly by an ophthalmologist.

Some of the common causes of leukocoria include: [4][8]
- Retinoblastoma.
- Coats disease.
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)
- Persistent fetal vasculature (PFV)
- Ocular toxocariasis and toxoplasmosis.
- Astrocytic hamartoma.
- Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR)
- Vitreous hemorrhage.
- Pediatric uveitis, an inflammation in part of the eye.
- Medullated retinal nerve fibers (MRNF), which happen when certain nerve fibers in the eye get a myelin sheath.
- Medulloepithelioma, a rare tumor in the eye.
- TORCH syndrome, which stands for Toxoplasmosis, Other agents, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes simplex. These are infections that can pass from a pregnant woman to her baby.
Treatment Options for Leukocoria [9]
The treatment of retinoblastoma may involve a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, laser therapy, and enucleation (removal of the eye) in severe cases. The choice of treatment depends on the size and location of the tumour and whether the disease has spread beyond the eye.
Reference:
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/leukocoria
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leukocoria
- allaboutvision.com/conditions/leukocoria
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560794
- eyewiki.org/Leukocoria
- sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/leukokoria
- webmd.com/eye-health/what-is-leukocoria
- mdsearchlight.com/eye-health/leukocoria
- medicoverhospitals.in/diseases/leukocoria





 وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی عینک شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است که اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با عینک , چشم، لنز، سلامتی چشم و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریهای چشمی، کنترل و درمان آن را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.